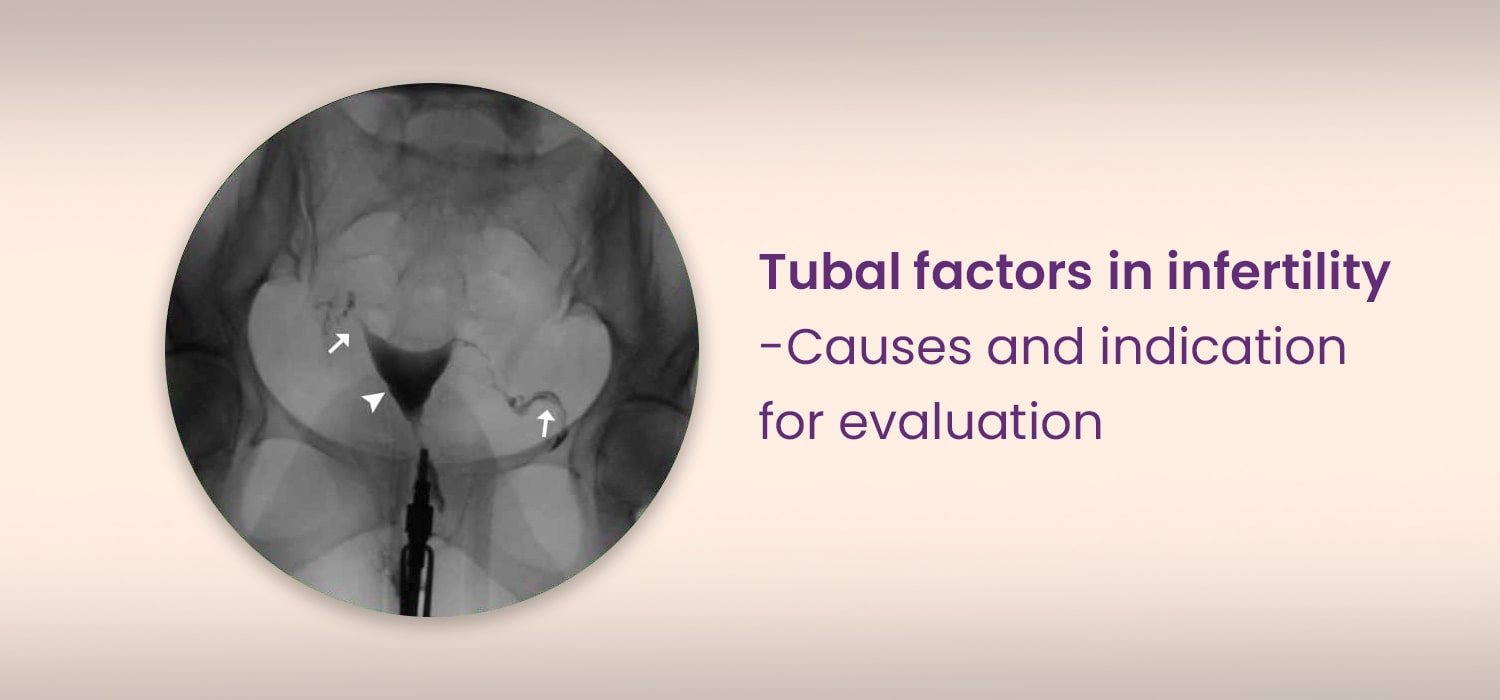
Tubal factors in infertility-Causes and indication for evaluation
The causes of tubal subfertility are always due to acquired factors. These include proximal/ mid or distal tubal disease which is often due to pelvic inflammation. Congenital tubal factors causing subfertility are rare...
Read MoreAdolescent Endometriosis: Early Onset, Diagnosis, and Treatment
EOE ( Early onset endometriosis) starting at the time of menarche or early adolescence may at times be severe, requiring early diagnosis and proper treatment. Its origin may be different from its adult variant and is attributed to NUB (Neonatal Uterine bleeding)...
Read MoreClinical Features and Diagnosis of Endometriosis: Symptoms and Diagnostic Methods
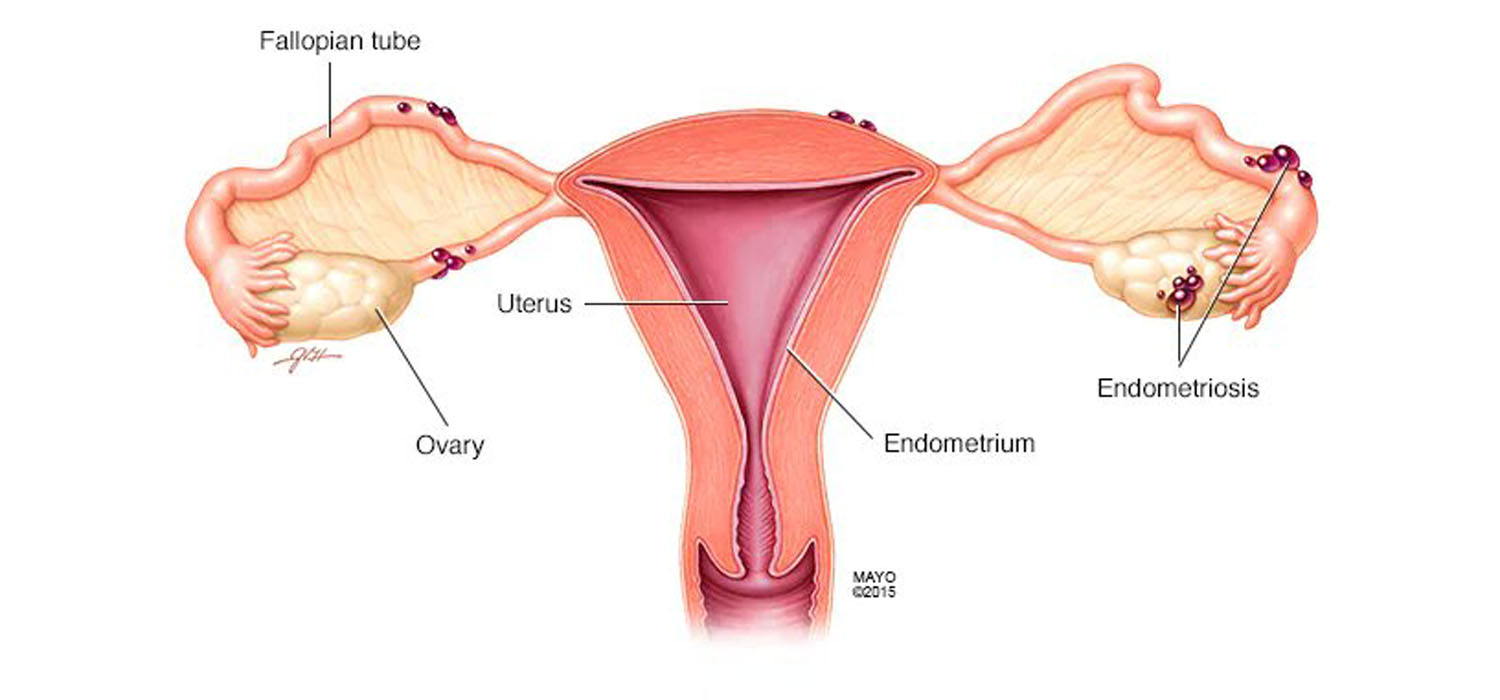
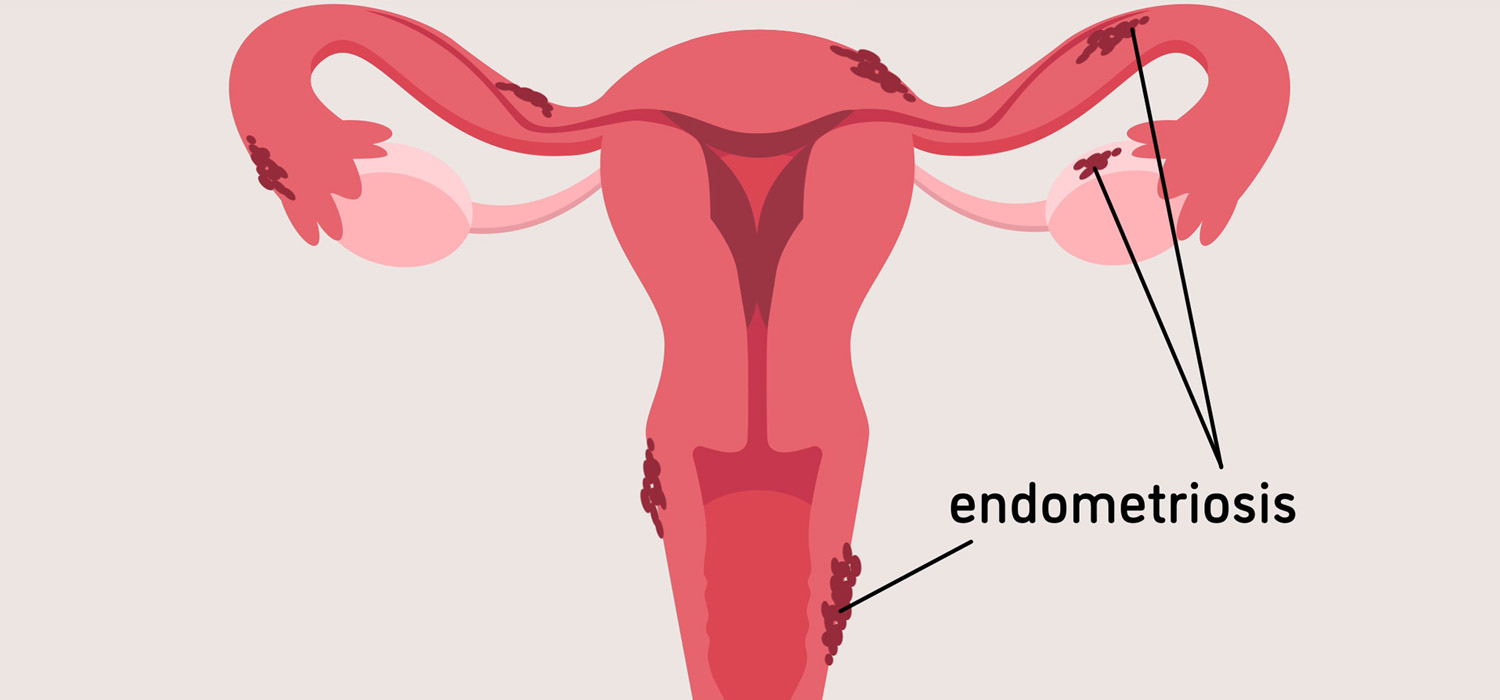
Endometriosis is a long-term, recurrent, debilitating challenge to therapy and affects 5-10% of women. It is characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma outside the endometrial cavity-on the pelvic peritoneum, ovaries, and the recto-cervical septum...
Read MoreGenomic Imprinting: Mechanisms, Characteristics, and Associated Conditions
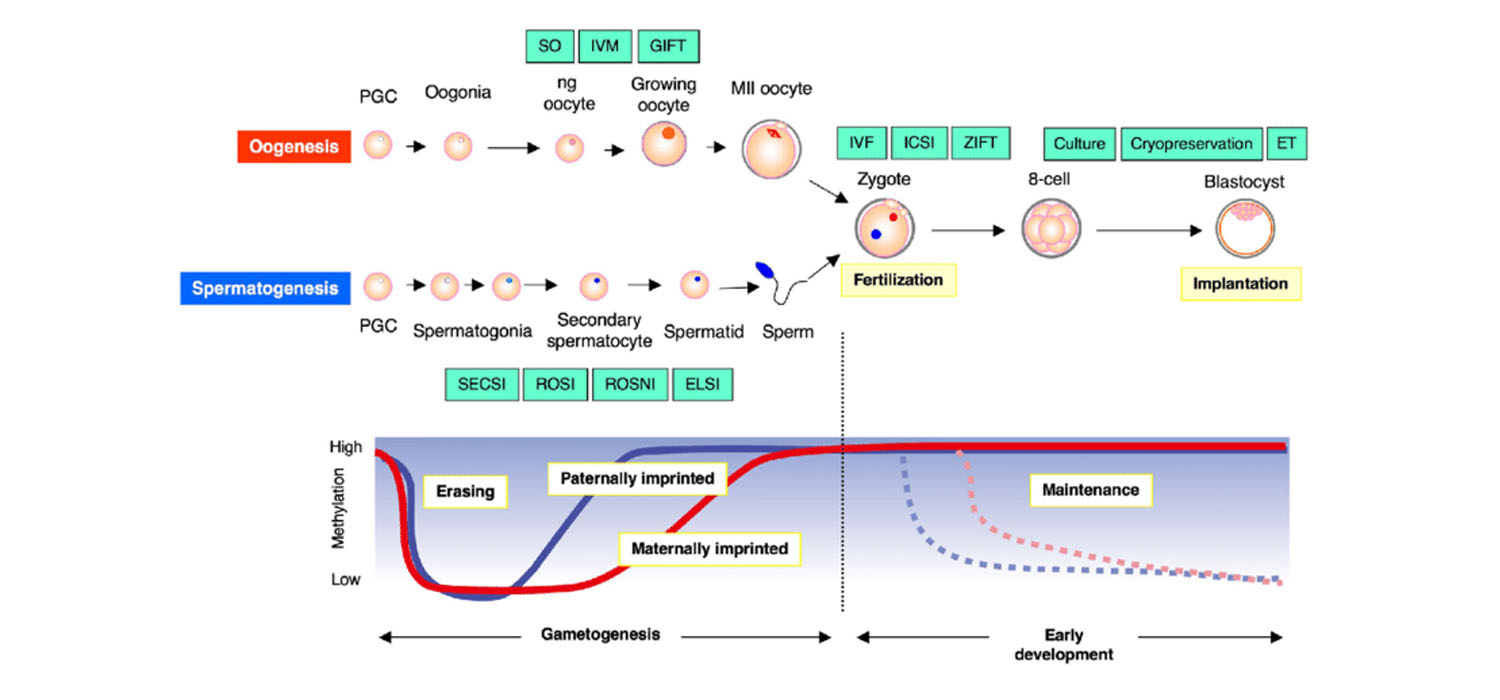
Genomic imprinting is a modification of the genome, selectively allowing genes from only one parental allele to be expressed. The underlying mechanism is mostly epigenetic. That means the DNA sequence is not changed but the alleles are expressed in a different way. Alleles are stamped by epigenetic influences that continue throughout pre- and peri-implantation phases...
Read MoreSemen Banking: Strategies for Optimal Cryopreservation and Storage
Semen banking is an integral part of reproductive medicine practice and involves storing ejaculated sperms at sub-zero temperatures. However, there is no internationally accepted gold-standard method that induces least damage to the sperms...
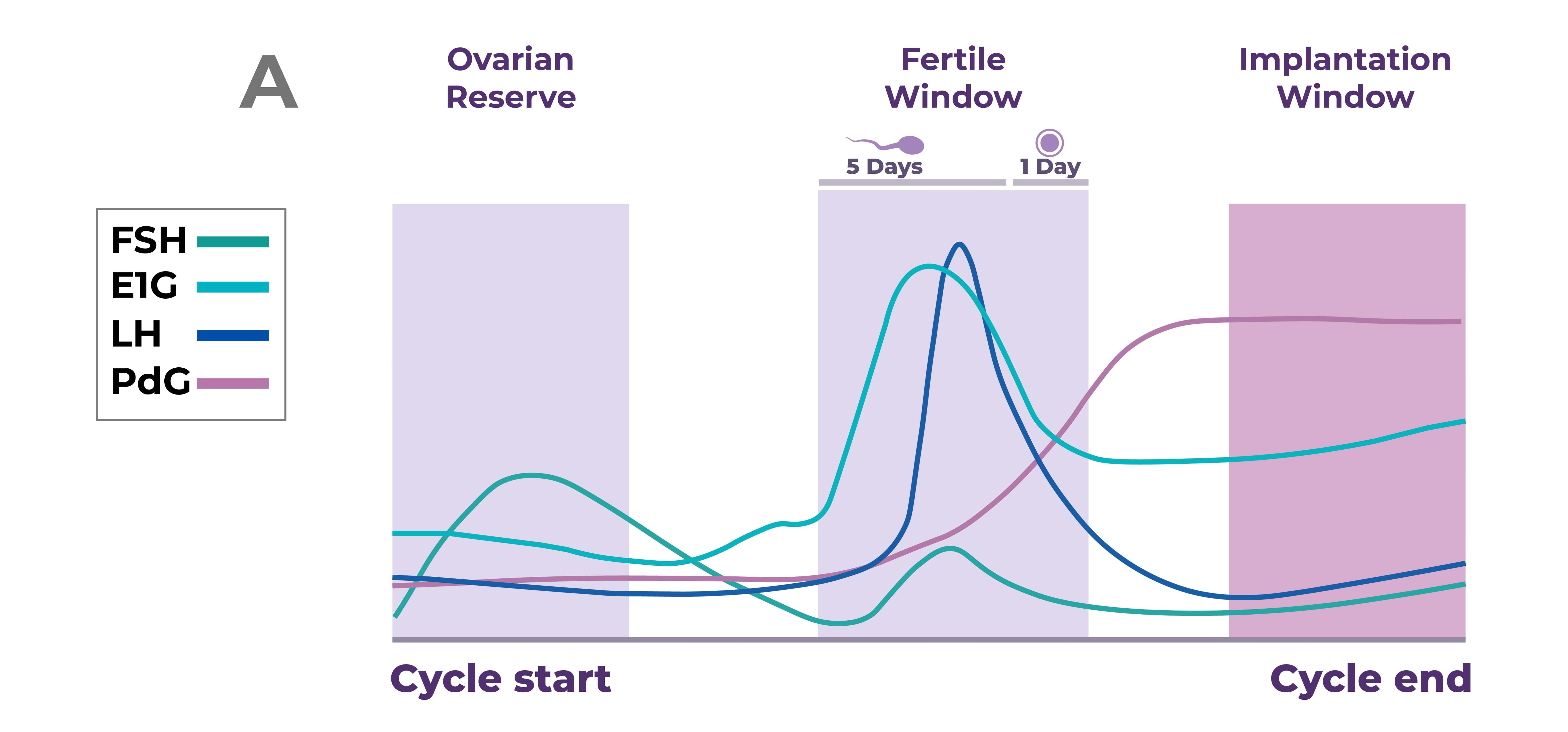
Read MoreMonitoring of Ovarian stimulation - Part 2
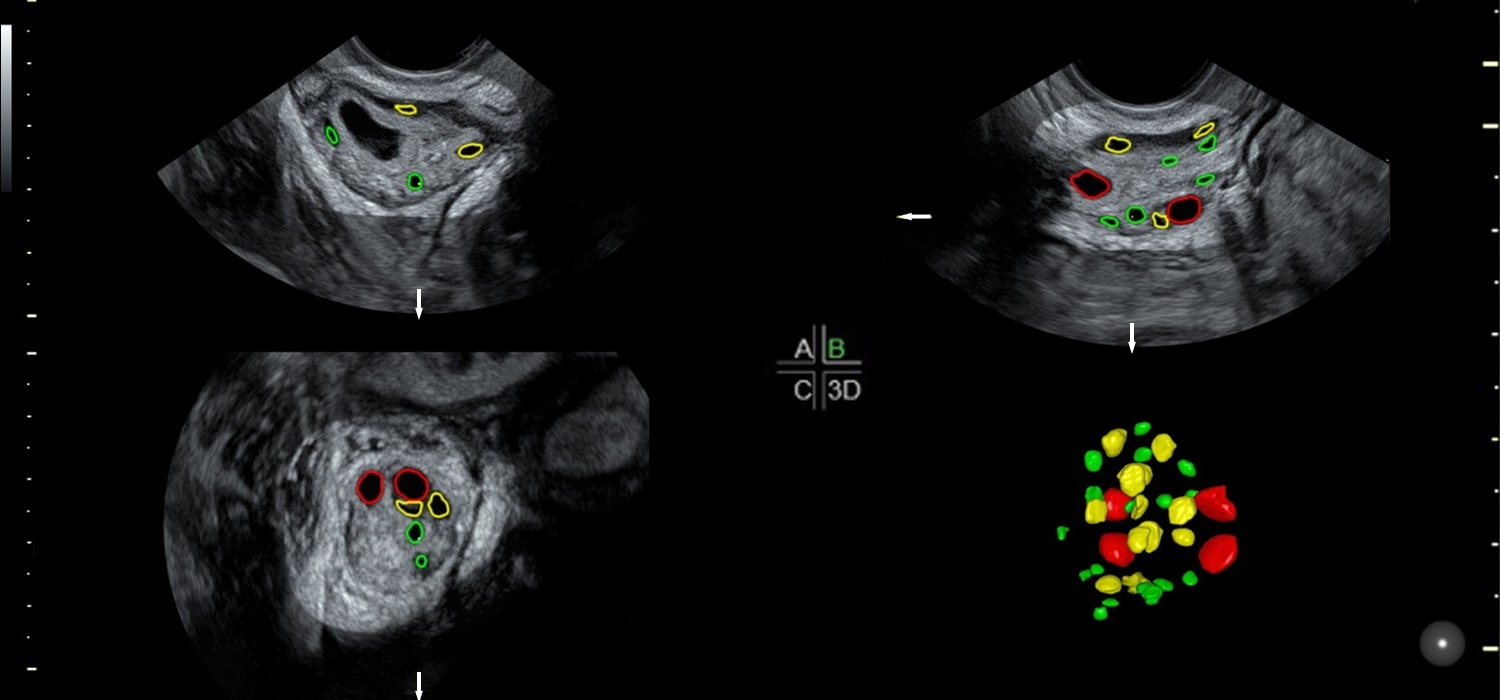
Ultrasound is quick, easy, non-invasive and not harmful to the oocyte. The transvaginal scan is preferred and the technique has been validated under normal,anovulatory and gonadotropin stimulated conditions...
Read MoreMonitoring of Ovarian stimulation - Part I
Monitoring of ovarian stimulation is necessary to optimise the outcome by modifying the dosage of stimulating medications and also to prevent complications like OHSS...
Read MoreEndometriosis - Clinical features and diagnosis
The diagnosis of endometriosis is challenging and an important reason for the delay in diagnosis. The GDG (Guideline development group) recommends that the diagnosis of endometriosis must be considered in women with any of the following...
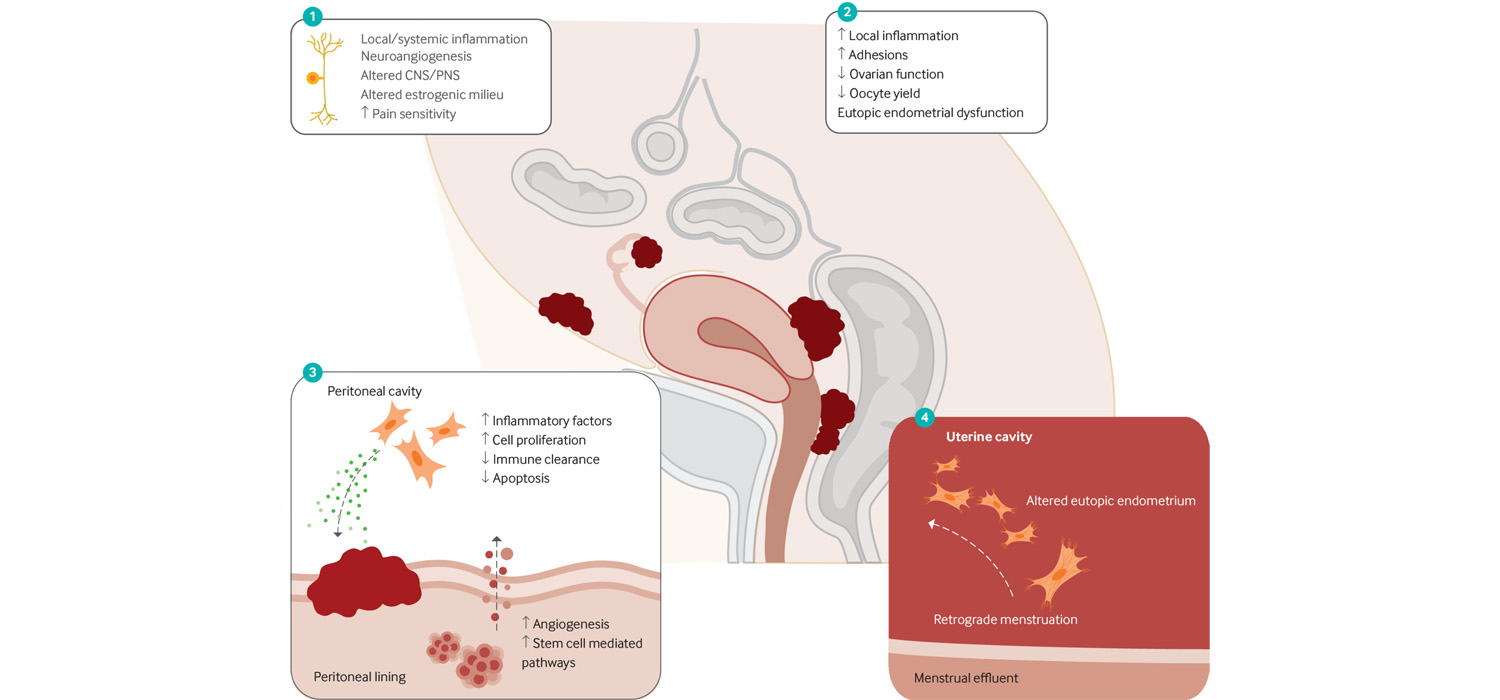
Read MoreEndometriosis Aetiopathogenesis
Endometriosis is a condition where endometrial stroma and glands are present outside the endometrial cavity, causing chronic inflammation, with fibrosis. It is often a long term, debilitating, recurrent condition which poses a challenge for therapy...
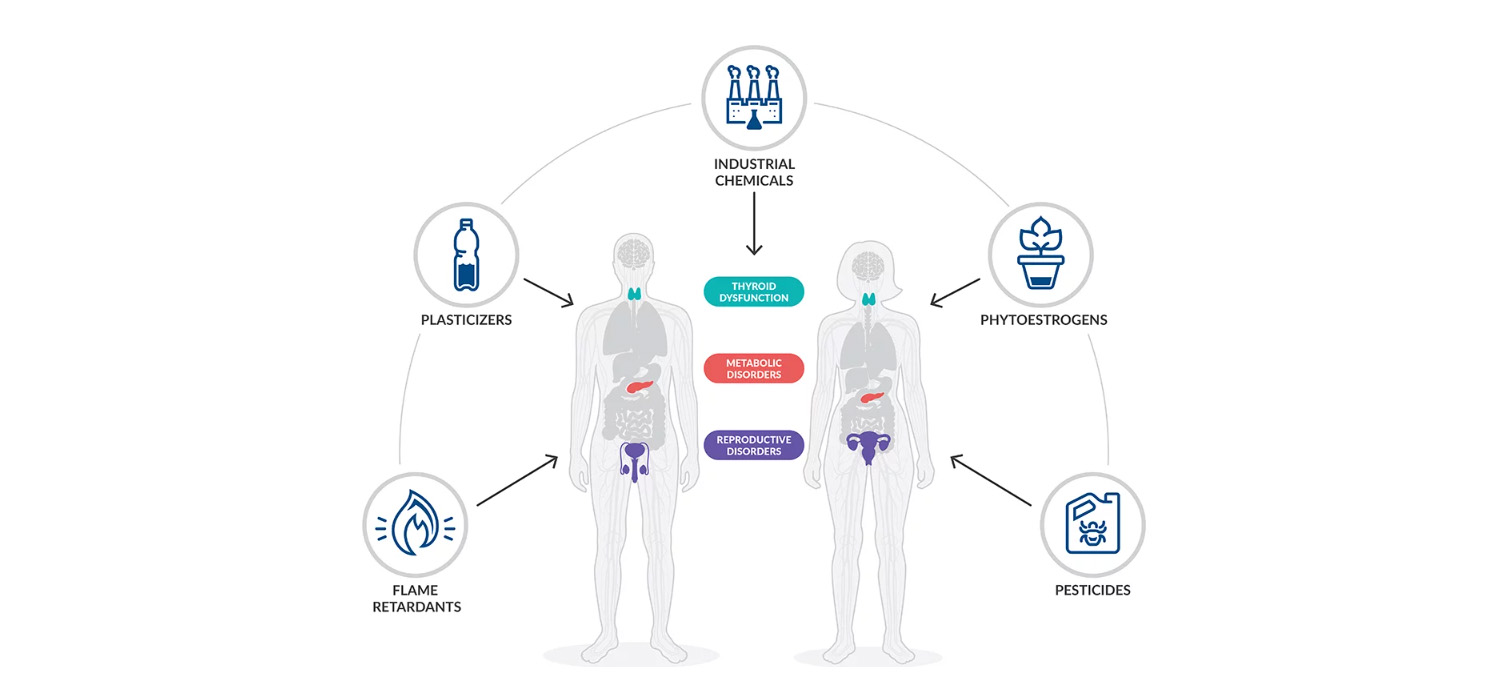
Read MoreEndocrine Disruptors in Infertility: Understanding the Impact and How to Avoid Them
Endocrine disrupting compounds (EDC) are the exogenous synthetic chemicals or a mixture of chemicals that interfere with any aspect of hormone action...
Read More