Clinical features and diagnosis of endometriosis
Endometriosis is a long-term, recurrent, debilitating challenge to therapy and affects 5-10% of women.
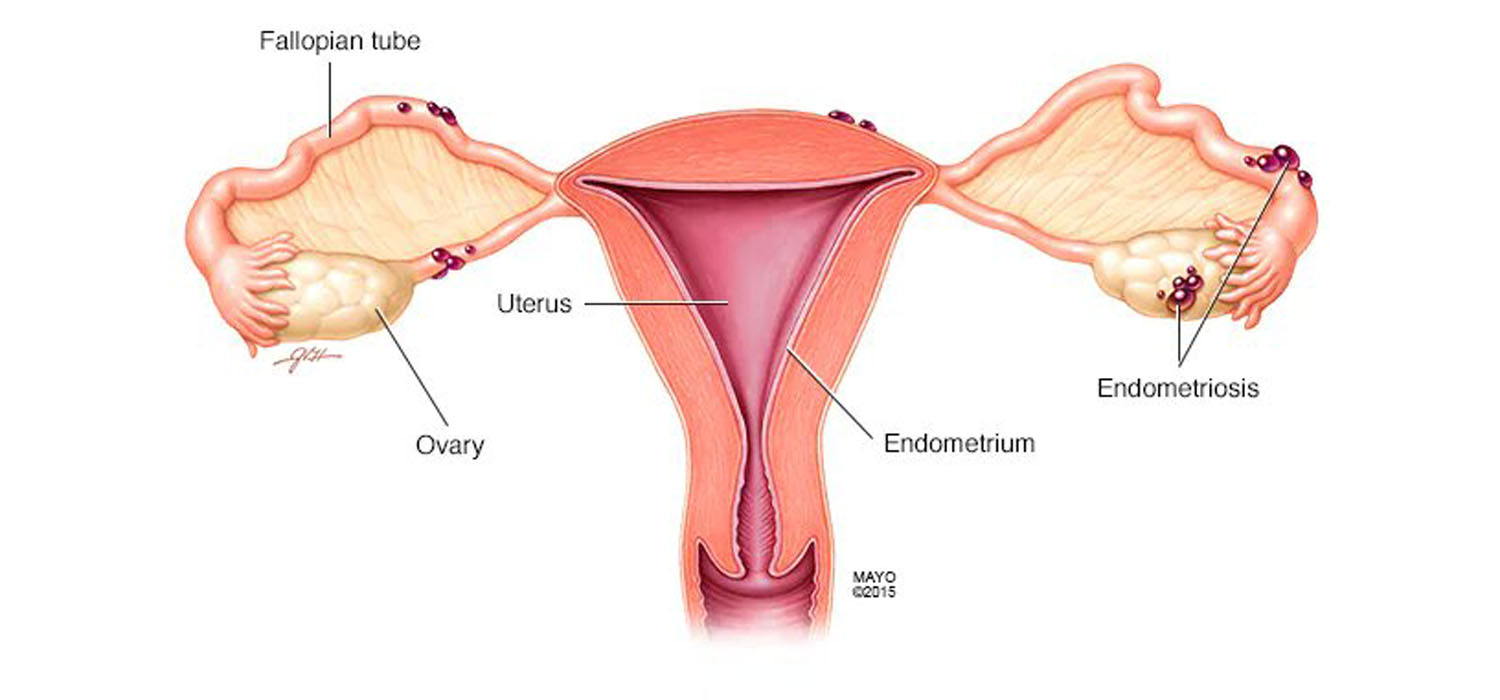
It is characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma outside the endometrial cavity-on the pelvic peritoneum, ovaries, and the recto-cervical septum.
The prevalence of endometriosis in normal women is 2-10% while it occurs in 20-50% of women with infertility. It is prevalent in over 60% of women with chronic pelvic pain and dysmenorrhea.
The maximum incidence is between 25-30 years.
Clinical features of endometriosis
The GDG (Guidelines Development Group) recommends considering the diagnosis of endometriosis with anyone of the following:
- Gynecological symptoms-Dysmenorrhea, Chronic pelvic pain, deep dyspareunia, infertility, fatigue
- Non-gynecological symptoms-Dyschezia, dysuria, hematuria, shoulder pain and rectal bleeding.
Diagnosis of endometriosis
- Clinical examination - Most times it may appear to be normal. However, a prevaginal or per-rectal examination can give a clue about it. Painful induration and/or recto-vaginal wall nodules felt or seen in the posterior vaginal fornix may be features of deep endometriosis. An adnexal mass of an endometrioma can also be present.
- Transvaginal Scan.
- Endometriotic nodules are not visible on a TVS. However, an endometrioma can be detected. A typical endometrioma appears like an oval mass, with hypoechoic contents and a hyperechoic wall and no papillae within. An endometrioma can also show atypical features like septae, papillae, non-homogenous content with irregular internal wall.
- Doppler Ultrasound - Hilus sign - presence of vessels between the cyst capsule and ovarian parenchyma is a feature of endometrioma.
- The differential diagnosis of an endometrioma includes a cystadenoma, dermoid cyst, hemorrhagic cyst, luteinized unruptured follicle and a corpus luteal cyst.
- 3D ultrasound for diagnosis of rectovaginal endometriosis is not a well-established tool yet.
The following table guides the diagnosis of endometrioma:
| Endometrioma | Corpus luteum | Cystadenoma | Dermoid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Septae | Infrequent | No | Frequent | Infrequent |
| Inhomogeneous content | Infrequent | Frequent | Rare | Frequent |
| Posterior reinforcement | No | No | No | Frequent |
| Hypoechogenic dots | Frequent | No | No | No |
3. MRI- Useful in the diagnosis of extraovarian endometriosis
4. CA-125 or other biomarkers in endometrial tissue, follicles, menstrual blood must not be used for diagnosis of endometriosis.
5. Laparoscopy with HPE of the tissue was considered as gold-standard for diagnosis. However, ESHRE 2022 guidelines do not consider it as the diagnostic gold standard any longer. Laparoscopy has been recommended only in the event of a negative imaging and/or when empirical therapy was unsuccessful or inappropriate.
For more info, Visit : www.medlineacademics.com