Disorders of puberty-Precocious Puberty
Development of secondary sexual characters before 8 years in girls, and before 9 years in boys, qualifies as precocious puberty.
There are 2 broad classifications for the cause of precocious puberty- central and Peripheral.
Central precocious puberty occurs because of increased gonadotropin secretion whereas peripheral precocious puberty is secondary to disease of the ovary or adrenals.
Precocious puberty is set to be Iso-sexual when the secondary sexual characters are appropriate for the child’s sex of rearing. It is said to be heterosexual when the secondary sexual characters developing are opposite to the phenotypic sex of the child.
Central precocious puberty is always Iso-sexual while the peripheral precocious puberty can be iso-sexual or heterosexual.
Precocious puberty is 10 times commoner in girls than in boys.
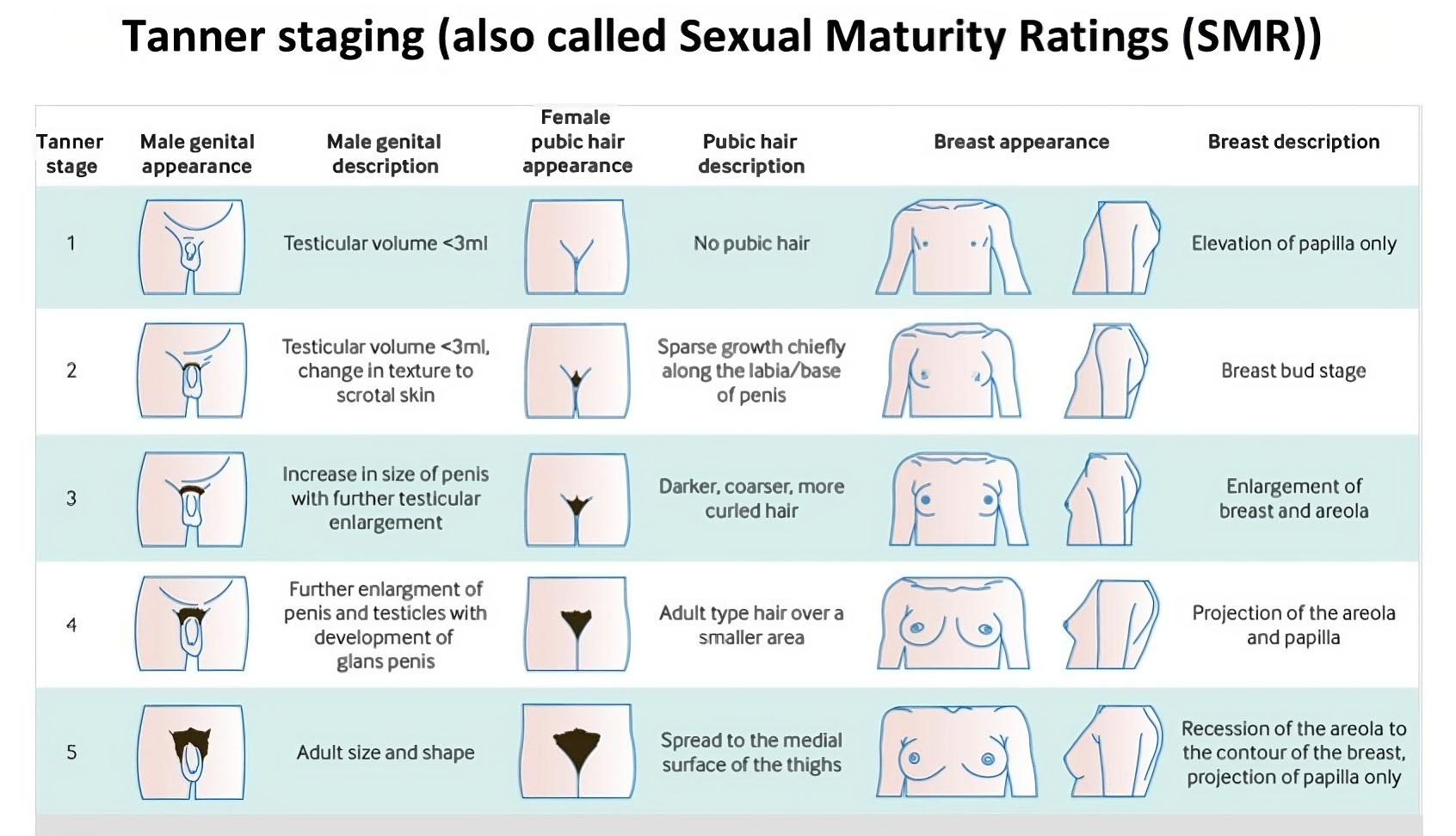
Clinical recognition of precocious puberty
- Progression from one Tanner stage to the next within 6 months.
- Early breast development in girls and increased testicular volume (>4 ml) in boys.
- Six months after onset, if features are progressive, it qualifies as precocious puberty. If stationary, it is considered to be a physiologic variant.
- Accelerated bone development- There occurs an early increase in height but the final attained height is reduced.
- Disparity in physical and psychological development- Smoking, drugs, sexual abuse, teenage pregnancy, sexually transmitted diseases and behavioural abnormalities like aggression and poor academic performance are often seen in these children and it is important to consider counselling them.
- Early puberty is also associated with increased risk of diabetes mellitus obesity and breast cancer.
Causes of Central Precocious Puberty (CPP or Gonadotrophin dependent precocious puberty)
This occurs in one in 5 to 10,000 children and is greater in girls. Causes include:
- Idiopathic-most cases
- central nervous system tumours or lesions
- Hypothalamic hamartoma-commonest cause
- Pituitary microadenoma
- Craniopharyngioma
- Ependymoma, Pinealoma, optic astrocytoma, optic glioma, arachidonic cyst.
- Hydrocephalus, Encephalocele.
- Neurofibromatosis
- Abscess, encephalitis, trauma, CNS vascular malformations or infections.
- Other causes- genetic, cranial radiotherapy, chemotherapy, primary hypothyroidism, endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDC) and obesity.
Causes of peripheral precocious puberty (Gonadotropin independent or pseudo precocious puberty)
- Gonadal Causes- Ovarian cysts, Ovarian tumors ( Granulosa/ Theca cell tumors, Germ cell tumor), Mc Cune Albright syndrome, Leydig cell tumor, Familial testotoxicosis (activating mutations of LH receptors)
- Adrenal causes- CAH, Adrenal functional tumors, Familial glucocorticoid resistance.
- hCG producing tumors- Chorio-carcinoma.
- Others-Exogenous hormones, FMPP ( Familial male-limited precocious puberty)
- History - age of onset, sequence of pubertal stages, family history of parents and siblings, timing of puberty, personal history of neurological symptoms like headache, seizures, behavioural changes, steroid exposure, and social history are relevant.
- Examination - The growth velocity is chartered as cms/yr, BMI, Tanner staging, signs of virilization, central nervous system and fundus examination, per abdominal examination and genital examination must be carried out.
- Biochemical testing - FSH, LH, Estrogen, Testosterone, TSH, FT4 and Prolactin estimations are done. Gonadotrophin stimulation test (LH > 5miu/L after gonadotropin administration – suggestive of PP). Testing for adrenal steroids like DHEAS and 17 KS and ACTH stimulation tests are also performed when needed.
- Imaging - X ray of the left wrist, skeletal survey with bone scans, CT/ MRI brain, CT of adrenals and pelvic ultrasound may be considered according to the cases.
- Progression of puberty staging in 3 to 6 months
- Growth velocity over 6 centimetres per year
- Bone age advancement more than 2 standard deviations.
- Uterine volume more than 2ml, length over 35 mm and thick endometrium.
- Ovarian volume more than 2 to 3 ml
- LH more than 5 mIU/L after gonadotropin stimulation. FSH/LH ration more than 0.66 and basal LH over 0.3mIU/L and detectable basal estrogen.
- MRI of the cranium / pituitary especially in girls before 6 years and in all boys, and if neurological symptoms are present.
- Fundus Examination for visual fields and papilledema.
- Baseline investigations include estimation of FSH, LH and sex steroids-namely estrogen and testosterone. Pre pubertal levels of LH is less than 0.1 mIU/L. Values over 0.3mIU/L implies CPP.
- X ray of left wrist- When the bone age is more than 2 SD than the chronological age, it implies progressive CPP.
- Pelvic ultrasound when the uterus is more than 3.5 centimetres with a thick endometrium and when the shape has changed from pre pubertal to pear shape it implies progressive precocious puberty.
- Surgical excision of any CNS tumours
- Medical therapy is indicated for majority cases of True precocious puberty ( also called Idiopathic precocious puberty- IPP)
- GnRH analogues -
Can be used in IPP and in GnRH hamartomas. It is used only if precocious puberty is progressive and has set in before 6 years of age. The GnRh analogues suppress the HPG axis, pause pubertal development, retard bone maturation, and stop early fusion of the epiphyseal plates, thus preserving the height potential. GnRH agonist treatment has significant impact on the final height as adults.
Long acting GnRh analogues are the gold standard in the treatment of idiopathic precocious puberty. Leuprolide acetate depot is given at the dosage of 3.75 mgs IM or SC once every 28 days (for child over 20 kilos). The child is monitored for pubertal stages, growth velocity and skeletal maturation. The dose may be increased by 7.5 milligrams if condition is still progressive at follow up.
The HPG axis restarts within 3 months after the stopping of therapy and has no negative impact on bone mineral density. Gonadal functions are restored after completing the therapy. - Newer advances
Sub dermal Histrelin 50 mg implant is used for long term therapy of more than one year. Extended release Leupride acetate 11.25 milligrams once in 3 months is also being used. months.
Counselling forms an important part of treatment in all these cases.
- GnRH analogues -
An Imprinting disorder is associated with MKRN3 gene which causes familial central precocious puberty. In this imprinting disorder, maternal genes are suppressed, and inheritance is from father. This gene is located on chromosome 15, near the gene for Prader-Willi syndrome. The average age of presentation is 6 to 8 years.
Small for gestational age, Intrauterine growth retardation, Low birth weight girl babies are prone for early onset menarche and puberty.
Evaluation of precocious puberty
Criteria to identify girls with progressive precautious puberty.
Approach to patients with central precocious puberty.
Treatment of central precocious puberty
Treatment of peripheral precocious puberty
PP is rarer than CPP. Incidence in girls 1:400 to 1:1000. The sex hormones from the gonads or the adrenals maybe produced autonomously, or they can be of exogenous origin like from environment or drugs
Hence, treatment is directed towards the underlying cause.
Tumours of ovary and adrenals are excised by surgery. Steroids form the mainstay of treatment in CAH. Hypothyroidism merits appropriate supplementation
McCune Albright syndrome
This is a rare genetic disorder characterised by 3 features namely- Cafe au lait spots, fibrous polyostotic dysplasia and peripheral precocious puberty. There is an increase in Estrogen and reduction in gonadotropins. This occurs because of mutation in GNAS1 gene which is involved in cAMP production at various tissue sites. The Cafe au lait spots have jagged borders and the spots do not cross the midline.
Peripheral precocious puberty (PPP) is due to functioning ovarian cysts that produce estrogen. The bones may show fibrous dysplasia and the bone age may be normal even though there is short stature. The treatment is challenging because of the heterogeneous presentation. cyproterone acetate and medroxy progesterone acetate are used in control bleeding. Letrozole and Tamoxifen have been tried. Anastrozole with leuprorelin has shown to increase the predicted adult height in girls with this syndrome.
FMPP (Familial male-limited precocious puberty or Testotoxicosis)
This causes Iso-sexual precocious puberty due to the activating mutation of LH. Autosomal dominant sex-linked inheritance is the mode of inheritance.
Presentation occurs below 4 years of age with rapid growth, testicular enlargement, and appearance of pubic hair. Presentation is heterogeneous with varying degrees of severity. The lab test shows hypogonadotropic hypergonadism picture that is, increased testosterone and reduce gonadotropins. Treatment is with spironolactone. Testolactone which is an aromatase inhibitor and ketoconazole normalise growth, bone maturation and improve predicted adult height in boys.
PCOS
Polycystic ovaries can also show precocious puberty because of hyperandrogenism and hyperinsulinemia. It is managed accordingly.
