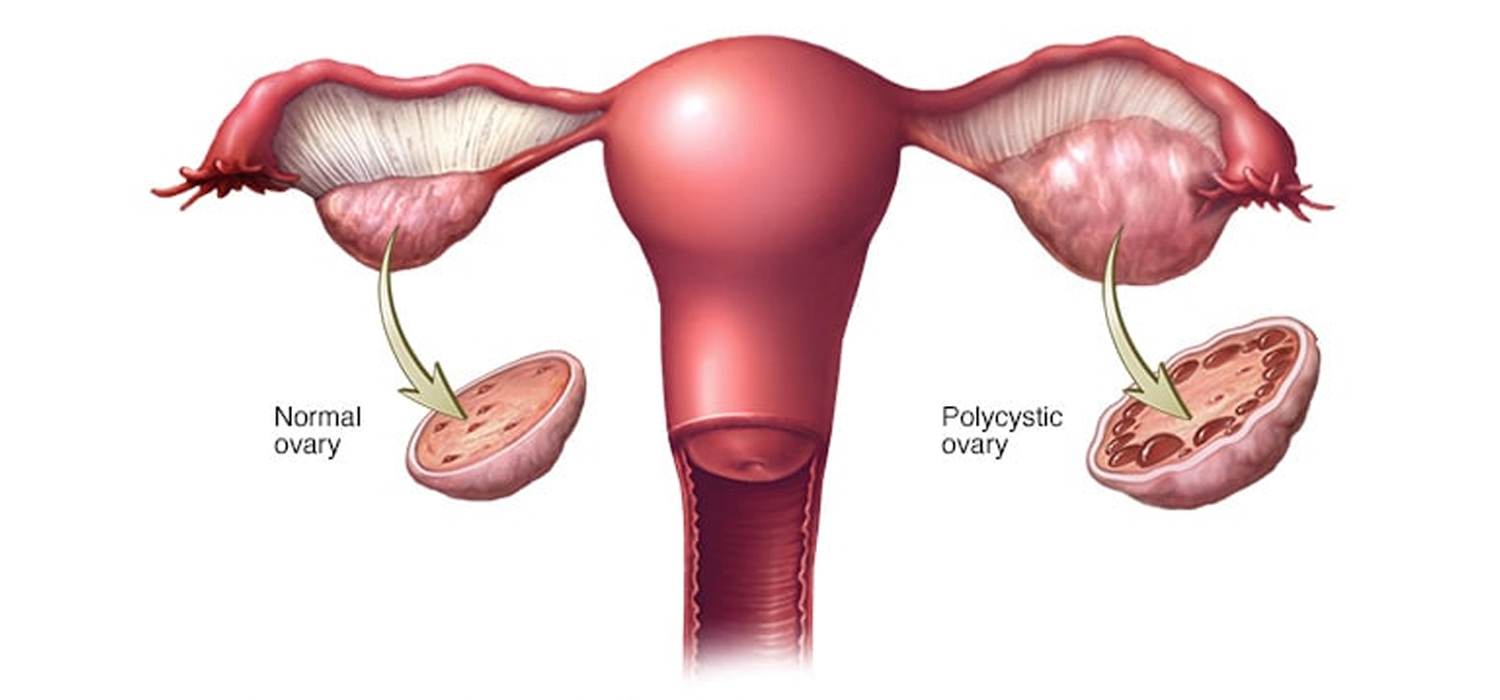
Unusual changes in a female body - PCOD or PCOS?
Often used interchangeably; PCOD and PCOS are the two words we hear frequently. It is important to understand the difference because having one of the condition does not necessarily mean you have the other. The risks and treatments, for both these dysfunctions, are very different albeit both are associated with ovaries and may sound the same. PCOD, read as Polycystic Ovarian Disease, is a hormonal disorder, where the ovaries contain many immature and partially matured eggs, which may eventually convert to cysts over a while. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) also termed as the Stein-Leventhal syndrome, is an endocrine and metabolic disorder obstructing the ovarian functions.
Based on the data stated in the Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism; Disorders such as PCOD and PCOS usually strikes at an early age affecting 5-10% of the women in their reproductive age. Sedentary lifestyle changes deeply affect the hormonal cycles. Genetic studies conducted by various institutes across the globe hints that hormones are also affected by genes. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) work on the tissues of a female body. Elevated levels of androgens and lower secretions of estrogens, often expose us to the risks of hirsutism (a condition known to cause excessive male hair growth patterns) and endometrial hyperplasia which further may induce endometrial cancer. Excess of androgen results in mounting dangers of fatty liver, hypertension and cardiovascular disease. The insane imbalances in hormone escalate manifold complications like irregular menstrual cycles, obesity, anxiety, sleep apnea and acne; but the traits may differ for every woman.
How is it diagnosed?
Blood tests are normally recommended to analyse the hormone levels. Individual tests are not enough to determine whether you have PCOS but Pelvic examinations scanning the abnormalities in the reproductive tract and an Ultrasound helps to examine the ovaries and thickness of the lining of the uterus.
A Puzzle that's part of our story- Can this condition lead to infertility?
PCOD is not considered an obstacle to fertility and conception may not be difficult. PCOS is an endocrinal problem and one of the most common causes of infertility and subfertility in women. Some other complications include pregnancy-induced high blood pressure, premature birth and miscarriage. American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists affirms that; Infertility affects 80% of the women with PCOS. Yes, PCOS is a leading cause of infertility, but patently treatable.
Treatments such as folic acid therapy and lifestyle changes are recommended to prevent the risk of heart and foetal neural tube defects. Lifestyle modifications are one of the best ways to deal with PCOS. Active manner of living your life coupled with exercise and healthy food choices may ease the problems related to obesity and control the blood sugar levels.
Poor quality of oocytes is one of the common observations in PCOS patients. Folic acid is accredited for its pivotal role in treating infertility. Folic acid is also known to reduce the risk of occasional anovulation and menstrual disorders. Observations of NCBI suggests the success rate of boosting fertility was higher with a combined intake of folic acid and myo-inositol, rich in vitamin-B. Forbye, Clomiphene citrate and letrozole, are used as first-line treatment in pharmacological measures for infertility. Metformin, used for metabolic disorders works on the endometrium and controls the blood sugar level therewithal reducing the risks of miscarriage and assisting in better reproductive outcomes.
Second-line treatment for infertility like laparoscopic Surgery to remove cysts are considered when the first-line treatments fail or non-reactive to the manifestations. Observational studies by NCBI states that the recovery rate was about 76% within six months of the surgery. A combination of metformin and gonadotropins is also considered a second-line treatment and an effective remedy for sub fertile women.
Where both first-line and second-line treatments have disappointed the patients, the third line of treatment is prescribed. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is used as a last resort for treating infertility in a woman with PCOS. The eggs are removed from the ovaries and fertilised with sperms in a laboratory. On the successful formation of an embryo, it is put back into the uterus. Data put forward by PMC suggest that after successful IVF, PCOS patients had more active oocytes, but the fertilisation rate IVF cycle was lower in contrast to Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). The success of IVF cycles is also dependent on the age and obesity factor. The conceiving rates were found to be lower for women above 35 years of age.
IVM is proposed for women with greater risk of ovarian hyper stimulation syndrome (OHSS). In IVM, the immature eggs are collected and the maturation process takes place outside the body. IVM's are less expensive than IVF and less time consuming, but the pregnancy rates are also lower for the same. As reported by NCBI, the conceiving rate in IVM is 26.2% compared to 38.3% for IVF.
An early diagnosis, lifestyle modifications and appropriate treatments can help annihilate the traits and ease associated discomforts.