Sperm vitality tests
Sperm Vitality means the number of live sperms in the sample. For successful fertilization, the sperms ought to be alive and motile. Yet the semen sample may have live sperms that are not motile.
The 6th edition of WHO Laboratory Manual (2021) recommends testing for sperm vitality when less than 40% of sperms in the sample are progressively motile. When sperm motility is low, vitality becomes a crucial parameter to be measured since it helps to differentiate between the live non-motile and dead sperms.
The test has to be done as soon as the liquefaction is complete and within one hour of ejaculation. This is done in order to prevent dehydration and variation in temperature.
The vitality of sperms is identified by testing the integrity of the sperm membrane. This is done by the dye exclusion method or by hypo osmotic swelling method.
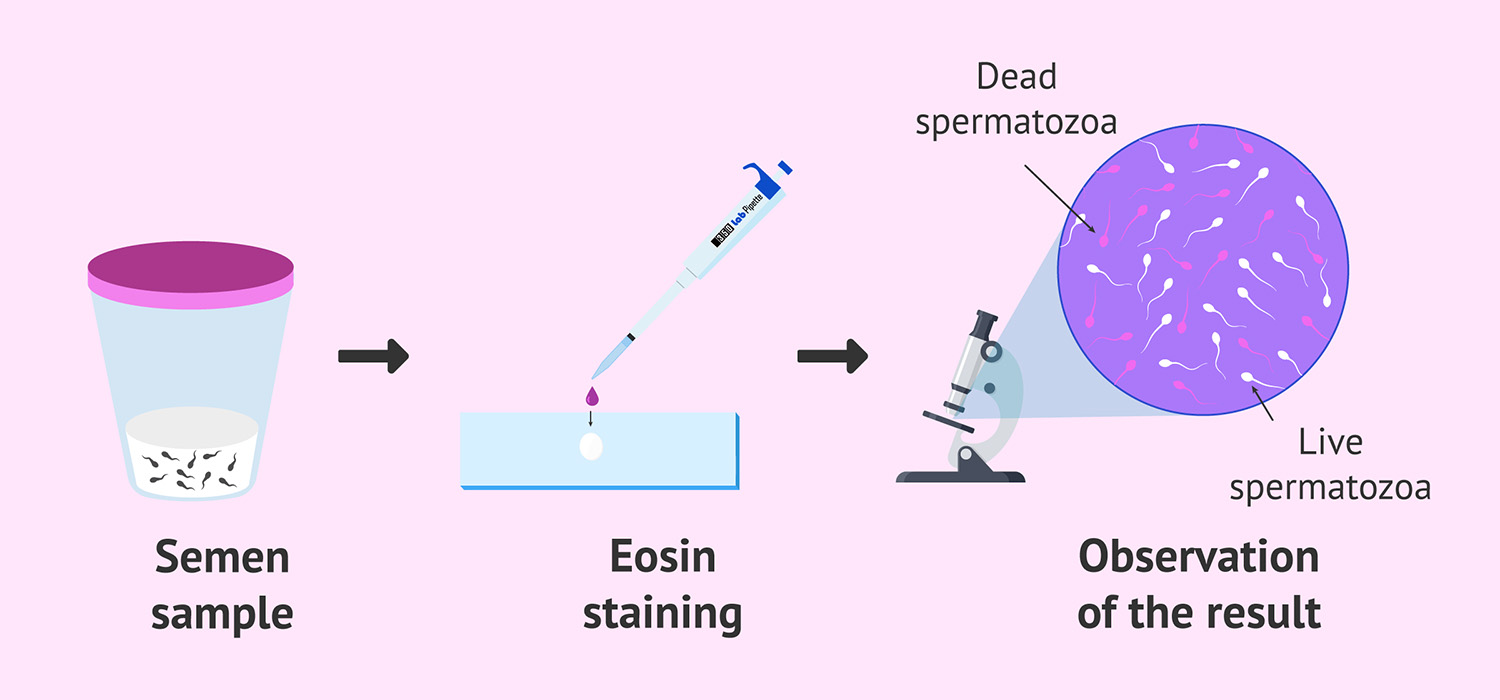
The dye exclusion method uses the dye Eosin alone or in combination with Nigrosin. This is based on the principle that damaged membrane allows entry of dye and live sperms do not.
When stained with eosin, the dead sperms take up the stain and are seen as pink or red. The live sperms do not take the dye and remain unstained. This can be used for wet smears and for sperm selection for ICSI.
Using Nigrosin with Eosin- Nigrosin provides dark background for easy assessment. The slides can be preserved for documentation.
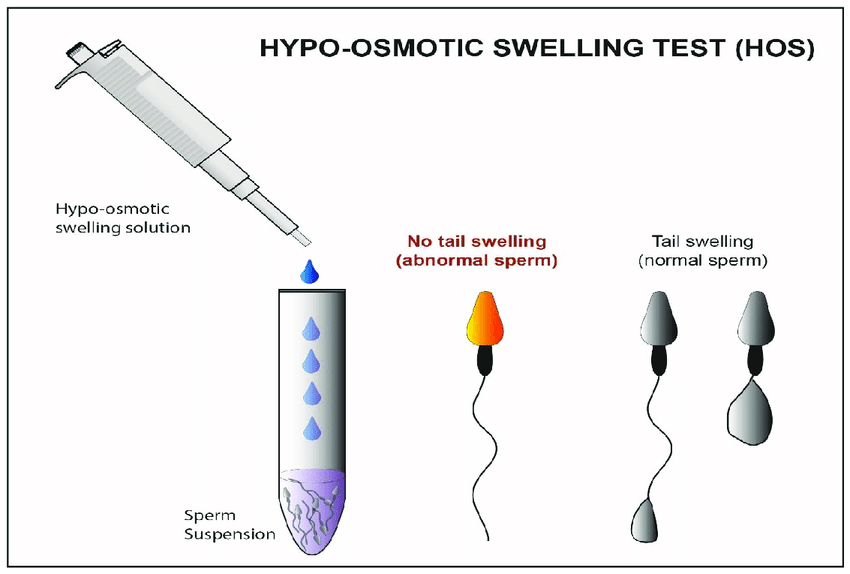
The hypo osmotic swelling(HOS) method tests the integrity of the membranes by studying the sperms in a hypotonic solution. HOS is based on the fact that damaged sperms have defective/ leaky membranes unlike the live sperms that have healthy membranes. The sperms are suspended in the hypo osmotic solution for about 30 minutes and studied. The dead sperms will appear to have a normal shape of the tails shape because of leaky membranes. The live sperms demonstrate swelling of the tails. At least 200 sperms are counted.
If the tail curling occurs in more than 58% of sperms then the sample is considered as normal. Tail curling in 50 to 58% of the counted sperms is intermediate and sample is considered abnormal for vitality if less than 50% of sperms do not have tail curling.
There also exits an inverse correlation between tail curling and sperm DNA fragmentation. Greater the HOS, lesser is the DNA fragmentation.
For more info, Visit : www.medlineacademics.com