PRENATAL SCREENING TESTS
NT Scan (Nuchal Translucency Scan)
It is an ultrasonographic fetal evaluation done between 11- 13+6 weeks of pregnancy. It offers many advantages including detection of NT, nasal bone (NB), tricuspid regurgitation (TR), and ductus venosus (DV). It can also be useful for accurately dating the gestation, assessment of early fetal anatomy, etc.,
A Nuchal Translucency (NT) scan measures the fluid build-up at the base of a baby’s neck which can help determine how likely it is that the baby has a congenital or genetic condition. It is the most important diagnostic marker for chromosomal abnormality. It is also imperative to remember that not all fetuses with increased NT are abnormal. Abnormal results do not mean the baby has Down syndrome or other congenital syndrome, it only means that the baby has a higher chance of having these conditions. Healthcare providers combine an NT scan with a blood test to more accurately assess the chance of carrying a genetically/chromosomally abnormal baby.
Double marker/dual marker test
A double marker test is a blood test that determines the baby’s risk of developing chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomy 21, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13. It is done up to 14 weeks of pregnancy. It measures serum levels of the following markers
Free βHCG – free beta human chorionic gonadotropin
PAPP-A – pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A.
Abnormal levels of the above markers are associated with an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities. Maternal blood levels of βHCG are increased in trisomy 21 while it is decreased in trisomy 18 and 13. When combined with maternal age the detection rate of fetal abnormalities is increased. Also, a Double marker test when combined with an NT scan is the best modality of screening test in detecting chromosomal abnormalities.
Other biochemical tests for fetal screening
Triple and quadruple screening tests are other biochemical tests done during the second trimester of pregnancy. Triple screening test measures for three markers, whereas quadruple screening test measures all three with an additional marker.
Triple screening test
It is a screening test with the potential to detect fetal chromosomal anomalies similar to a double marker test. It is done mainly between 15-20 weeks of gestation. It involves the measurement of three following markers.
- AFP - Alpha-fetoprotein
- hCG - Human chorionic gonadotropin
- uE3 - Unconjugated estriol
AFP is released by the fetus, hCG is secreted by the placenta and uE3 is released by both the baby and the placenta. The levels of these markers would predict the risk of the fetus having abnormalities as well as neural tube defects such as spina bifida etc.
Quadruple screening test
It is a second-trimester screening blood test done between 15-22 weeks of gestation. The results are most accurate between 16-18 weeks of gestation. It also detects the baby’s risk of having Down syndrome, neural tube defects, etc. However, when compared to triple screening tests the sensitivity of quadruple screening is high. This testing includes measurement of maternal blood levels of the following markers
- AFP - Alpha-fetoprotein
- hCG - Human chorionic gonadotropin
- uE3 - Unconjugated estriol
- Inhibin A - produced by the placenta
NIPT (Non Invasive Prenatal Testing)
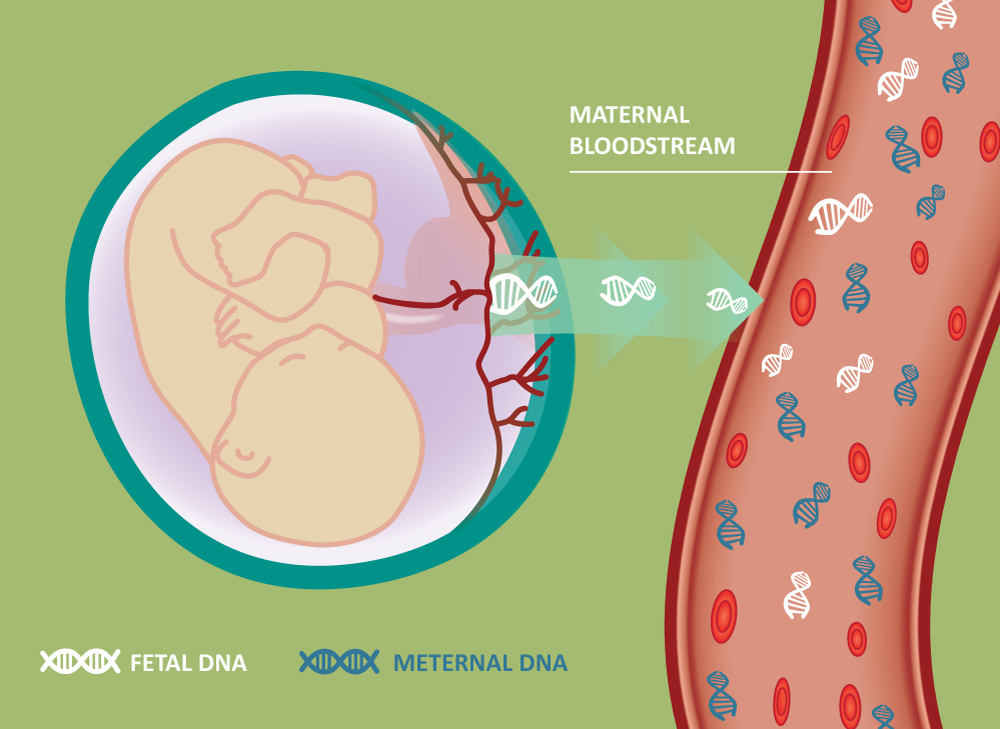
This test is based on analyzing fetal DNA present in maternal blood circulation. Fetal DNA, also called as cell-free fetal DNA (cfDNA) is released into the maternal blood from the syncytiotrophoblastic cells, cfDNA starts to appear in maternal blood as early as 5 weeks of gestation and can be usually measured at around 10 weeks of gestation. It is the most sensitive screening test for detecting trisomy 21. The proportion of cfDNA in the maternal blood is vital in the precision of test results. The main disadvantage of this test is that it is expensive and is not a primary screening test.
Integrated tests
Biochemical tests can be combined with the first-trimester ultrasound. The main advantage is that it has superior sensitivity in detecting abnormalities. Even though NT scan reports are interpreted by most healthcare provider on the same day, biochemical tests need extended wait time to access the results. Additionally, NT scans and biochemical tests are not diagnostic tests and they need invasive testing such as amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, cordocentesis, or fetal tissue biopsy for diagnosis. These diagnostic tests carry an additional risk of infection or miscarriage.
Who should undergo fetal evaluation for chromosomal abnormalities?
It is recommended all women regardless of their age/ risk factors be offered screening test for chromosomal abnormalities. However, the following category of women would benefit more,
- Women who are older than 35 years of age
- Women with a history of previous pregnancy with chromosomal abnormalities
- Women who are taking insulin to treat diabetes
To know more about the first trimester ultrasonography, join our first trimester ultrasound course.
For more info, Visit : www.medlineacademics.com