Overview of the Semen Preparation techniques in ART
In the management of infertility, it is imperative to ensure that the spermatozoa selected are of the highest quality in order to optimize or better the results in ART procedures. Morphologically normal, highly motile sperms free from unwanted cells and substances is the goal of semen preparations.
Need for preparing the semen for ART:
- To separate the sperms from the seminal plasma which contains prostaglandins, zinc, antigenic proteins that can interfere with pregnancy in IVF/IUI.
- Helps to remove decapacitation factors that might prevent the normal process of capacitation of the sperms.
- To remove dead sperms, leukocytes, and immature forms from the ejaculate.
- To reduce the concentration of cytokines, lymphokines and reduce formation of oxygen free radicles that are deleterious to sperms.
Shortcoming of semen preparation:
It is not 100% effective in removing in removing infectious agents and hence must be regarded as a biohazard to the handlers.
Ideal sperm preparation technique:
- Should be easy, quick, and cost-effective.
- Isolate as many motile spermatozoa as possible and eliminate the dead ones and other cells.
- Should not cause sperm damage or non-physiological alterations of the separated sperms during the process.
- Should be able to eliminate all toxic/ bio-active substances like ROS or decapacitation factors.
- Should allow for processing of large volumes of ejaculates.
Needless to say, since no single technique can fulfill all the criteria, various techniques are used. Also, the quality of the ejaculate had direct consequence on the choice of the sperm preparation technique.
Various techniques of sperm preparation:
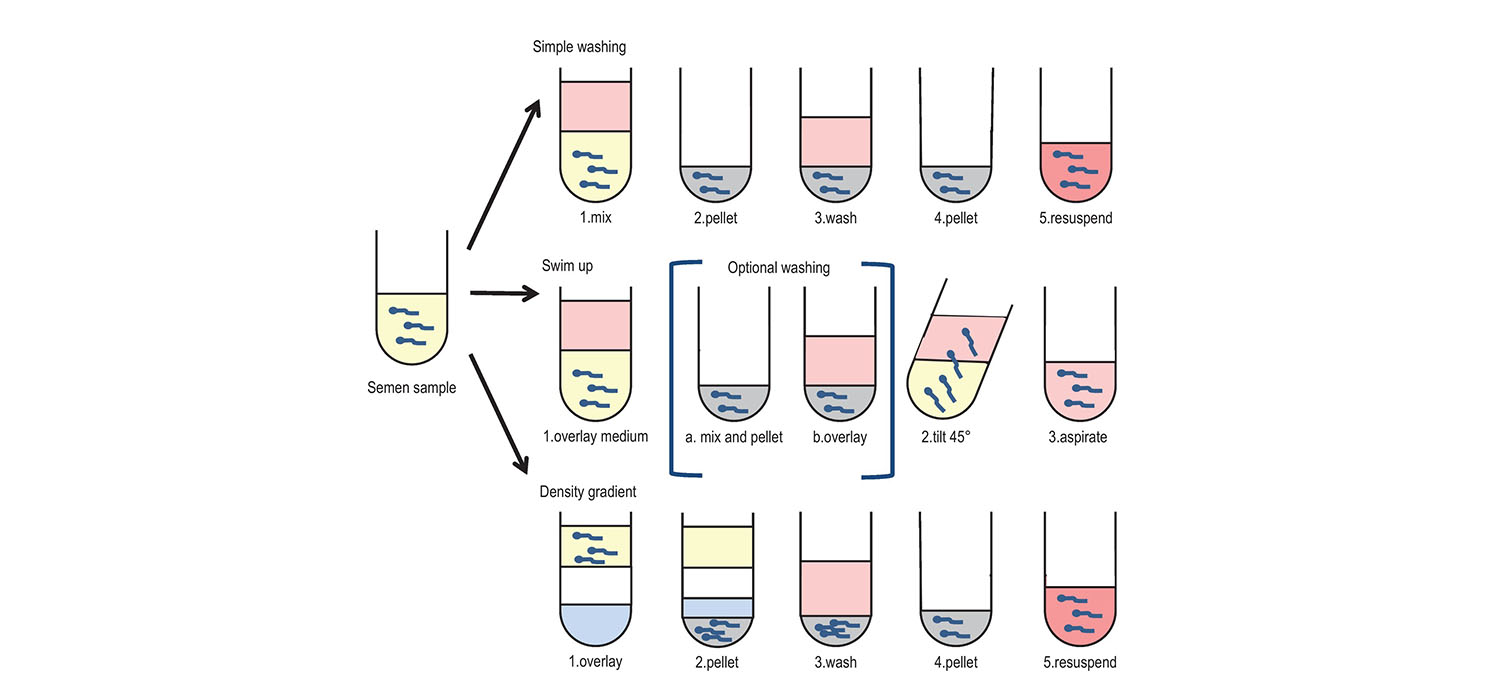
- Simple wash
- Migration based techniques:
- Swim-up
- Migration sedimentation
- Swim-down
- Density gradient centrifugation (DGC)
- Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MAC)
- Glass wool filtration
- Sephadex columns
- Transmembrane migration
Advanced strategies of sperm selection:
- Sophisticated techniques for assessment of sperm morphology
- MSOME ( Motile sperm organelle morphology examination) and subsequent IMSI (Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection)
- Using electrical charges:
- Zeta potential using flow cytometry.
- Molecular binding techniques
- Sperm binding to Annexin V
- Hyaluronic acid binding
- Microfluidics for isolating motile sperms.
- Sperm selection based on guidance mechanisms.
- Rheotaxis-flow thro a series of microchannels
- Chemotaxis-flow between wells using chemo attachment.
- Thermotaxis-Using temperature gradient to separate sperms.
When to use a particular sperm preparation
The choice of sperm preparation method depends on the characters of the semen sample.
- Sperm concentration & motility are within normal limits- Direct swim-up technique.
- Significant oligozoospermia, teratozoospermia & asthenozoospermia-DGC, Glass wool filtration
Preparation of Epididymal spermatozoa
Large number of sperms can be collected from epididymis. This sample usually does not contain non-germ cells like RBCs. DGC can be used if sufficient number of sperms have been collected. If the number of aspirated sperms is low, a simple wash technique is used.
Preparation of Testicular spermatozoa
Testicular sperms can be obtained by open biopsy or percutaneous needle biopsy. The sample contains large number of non-germ cells like RBCs. The elongated spermatids which are bound to the seminal tubules ought to be freed. Sperm cells from testes are used directly for ICSI because they are less in number and of poor motility.
Preparation of assisted ejaculation samples
Direct penile vibratory stimulation or indirect rectal stimulation ( electroejaculation)is used to retrieve the sperms in men having anejaculation due to various causes. Ejaculates obtained from electroejaculation are processed effectively by DGC. Semen obtained from vibratory stimulation is often better than that with electroejaculation. Semen sample of men with spinal cord injuries often has high sperm concentration with low motility and plenty of cellular contaminants like RBCs and WBCs.
Preparation of retrograde ejaculation samples
The patient is asked to urinate without entirely emptying the bladder. Then he is asked to ejaculate followed urinating in another specimen cup containing 5-6 ml of culture medium( which alkalinizes the urine). This urine sample is analyzed after centrifugation. The concentrated retrograde specimen and the antegrade specimen are prepared by DGC.
Limitations of conventional sperm preparation techniques
- Natural sperm selection that occurs at the various levels along the female genital tract is bypassed to varying extents.
- In ICSI, all natural barriers to fertilization are bypassed and sperm components that normally do not enter the oocyte are introduced. This could damage oocyte activation and embryo development.
- 3) Sperms with DNA damage can still fertilize the oocyte and may cause pregnancy loss.
Hence conventional sperm selection methods do not necessarily select functionally or genetically competent spermatozoa.
The search for an ideal sperm preparation method that selects sperms mimicking the natural selection process in the female genital tract that ensures a healthy sperm with the best fertilizing and genetic potential is still on and is far from over.