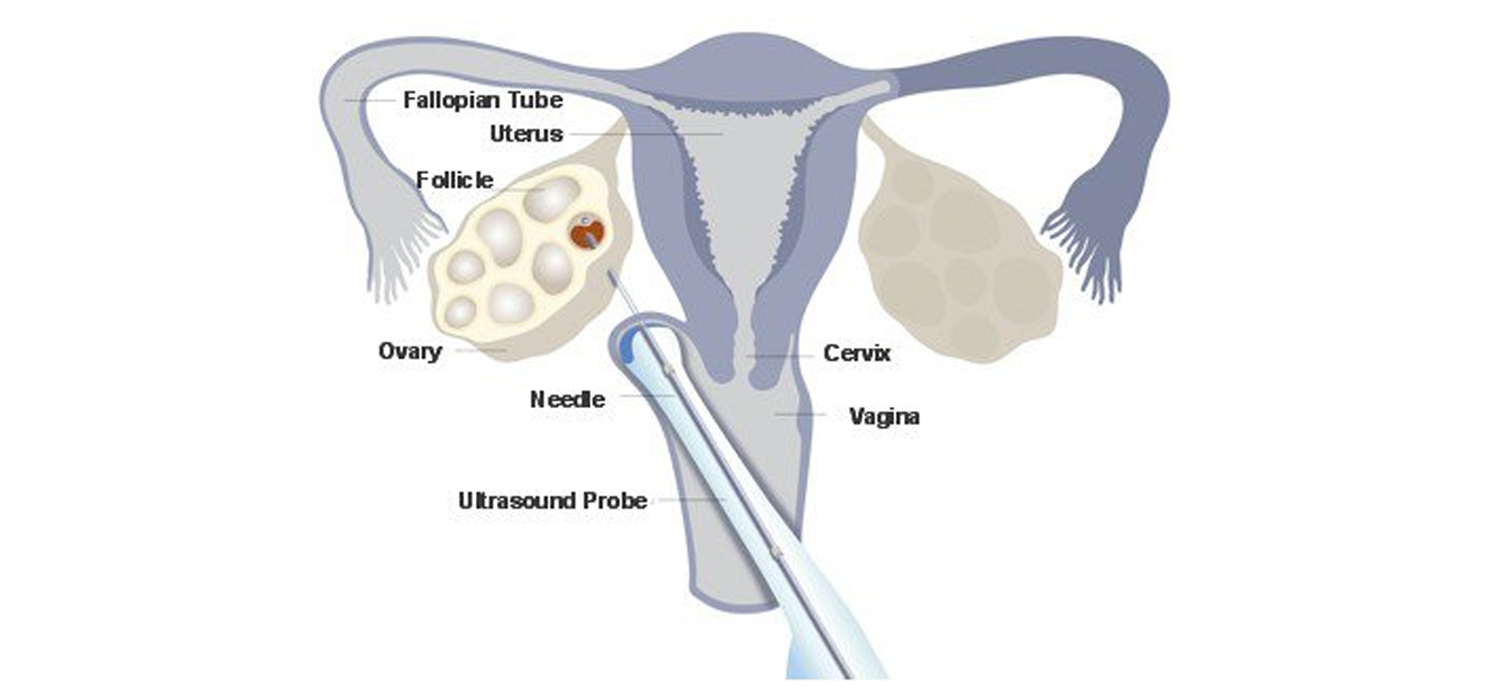
Oocyte retrieval
Oocyte retrieval (OR) or Ovum pick up ( OPU) is an ultrasound guided technique in which oocytes are aspirated using a needle connected to a suction pump. This can be done by abdominal or vaginal route.
History
The first ever oocyte retrieval was by Drs Morgensterm & Soupart in 1972. Drs Edward & Steptoe performed laparoscopic oocyte retrieval for their first successful IVF & birth of Louise Brown. Drs. Susan Lanz and Wilfred Feichtinger pioneered transvaginal oocyte retrieval (TVOR) which is now the popular method for routine oocyte retrieval
Transmyometrial and transabdominal routes can be reserved for cases with adhesions or abnormal ovarian placement.
Before the OR
- 1. To check if the trigger has been taken a advised
- 2. Inform the embryologist, anesthetist and OT staff about the planned OPU
- 3. Patient checklist includes-Correct identity, correct consent, recent hormone levels and ultrasound, review of stimulation and procedure plan
- 4. Instrument checklist include checking for proper functioning of scan machine, suction apparatus, foot pedal.
Patient preparation
- 1. Appropriate trigger 34-36 hours before OR
- 2. Confirm patient has taken trigger
- 3. Appropriate hormonal measurements as indicated
- 4. Recheck stimulation protocol.
Patient has to be nil oral for 6 hours and empty the bladder just before the procedure.
Anesthesia can be conscious sedation using Midozolam or Prpofol and general anesthesia is rarely used.
Partner’s sperm collection is done on the day of OR while a back-up frozen sample is available in case there is inability to produce semen on the day of OR.
Procedure:
Procedure involves retrieving the oocytes while performing the vaginal scan. The needle can be 16,17 or 18 G and the pressure for suction is 120 mm Hg. Immature follicles require lower pressure- around 40-60 mm Hg. A double lumen needle allows for flushing of the follicles.
The oocytes are collected in prewarmed test tubes.
Post-procedure
The ovaries are re-checked to ensure if all follicles have been aspirated. The pouch of Douglas is checked for any collection suggestive of blood and internal bleeding. Patient may be given analgesics and antibiotics as indicted. Luteal phase support with progesterone/hCG/GnRha is advised as per planned protocol. Couple are advised to return after 24 hours for information abut the success of fertiization and further plan.
Complications:
The common complications include hemorrhage and trauma to pelvis structures. The bleeding can be from the ovarian surface or due to injury to uterine, vaginal , ovarian or iliac vessels. Use of doppler can prevent vessel injury.
Pelvic infection , tubo-ovarian or pelvic abscess may been seen after 1-6 weeks. Risk of infectin increases in cases of endometrioma or with past history of PID.
Serious/ rare complications includes OHSS, ovarian torsion, rupture of ovarian endometrioma, anesthetic complications.
In conclusion, oocyte retrieval is an important step in the process of IVF and can be performed safely and satisfactorily.
For more info, Follow : medlineacademics.com