Hirsutism
There exist 50 million hair follicles on the human body and 1-1.5 lakhs follicles on the scalp. The three phases of hair growth are anagen (active growth), Catagen (involution stage) and telogen (resting stage after which hair falls off) Lanugo and vellus hair are non-medullated while the terminal haors are medullated and are longer, pigmented, and coarser. Conversion into medullated terminal hair is irreversible.
Factors regulating hair growth
Local and systemic factors - Growth factors and cytokines cause increase in matrix minerallo-proteins which act on dermal papilla to increase the hair growth. Thyroid and growth hormones vary the anagen to telogen ratio.
Sex steroids - testosterone and dihydrotestosterone act on androgen receptors and cause gene transcription.
Hirsutism is the sum total of interaction of androgens locally, circulating androgens and sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens.
Diagnosis of hirsutism
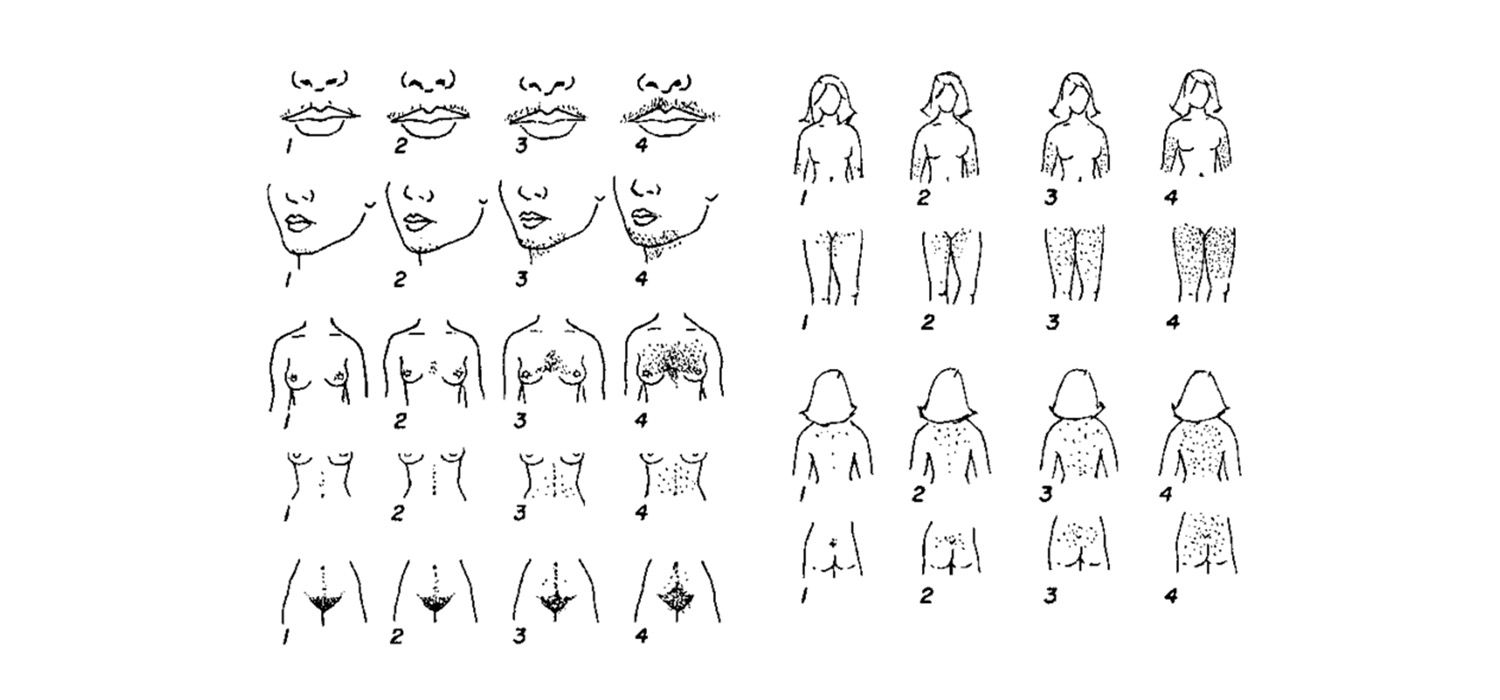
Modified Ferrimann-Gallway score is used for assessing the degree of hirsutism. Scores upto 15 is mild hirsutism, 16-25 is moderate and a score over 25 indicates severe hirsutism.
Aetiology of hirsutism
Causes of hirsutism man be classified as idiopathic, ovarian, adrenal, medication and miscellaneous.
4-7% of hirsutism are idiopathic where ovarian cycles and androgen levels are normal. The cause could be due to increased 5 alpha reductase or altered androgen receptors.
Ovarian causes include PCOS or hormone secreting tumours like Leydig cell/ hilus cell.
Adrenal causes are late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia or non -classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NC- CAH) and also neoplasms like virilizing adrenal adenoma or carcinoma.
Several drugs are implicated in hirsutism, and they include carbamazepine, clonazepam, steroids, diazoxide, estrogen, fluoxetine, lamotrignine, etc.
Hypothyroidism, acromegaly, Cushing’s syndrome, hyper-prolactinaemia, HAIR-AN syndrome are some of the endocrine conditions that may be associated with hirsutism.
History, physical examination of a case of hirsutism
Duration and onset of symptoms, menstrual disturbances, medication, weight gain, breast discharge, skin changes and family history are important.
Examination includes checking BMI, blood pressure, alopecia/ acne, skin changes like acanthosis nigricans, breast discharge, evidence of striae, moon-facies, and signs of virilization followed by per abdomen and per vaginal examination.
Hormonal evaluation
Free testosterone and total testosterone are measured, the former being more significant. The significance of measuring DHEA-S and DHEA is unknown.
NC-CAH can be confirmed by cosyntropin stimulation test and if 17-OHP is more than 1000 ng/dl.
Serum prolactin is estimated in cases with galactorrhoea.
Obese PCOS merit complete evaluation as per GDG recommendations by measurement of BP, waist circumference, BMI, lipid profile and 2-hr-75 gms glucose OGCT.
Ultrasound may be used for diagnosis if PCOS, NC-CAH and androgen secreting tumours.
Treatment of hirsutism
Treatment depends on the severity and distress it is causing to the patient. Patient must be counselled about recurrence and the need for prolonged treatment.
Treatment is local/ cosmetic and with medication.
Shaving, depilatory cream, waxing are temporary cosmetic measures while laser and electrolysis are permanent.
Medications for treatment include alpha reductase inhibitor like Finasteride, androgen receptor blockers like Spironolactone, Cyproterone acetate and Flutamide. Oral contraceptive pills containing ethinyl estradiol with cyproterone acetate or Drosperinone can also be offered. Eflornithine cream when used locally reduces hair growth.
Other medications that are used Insulin sensitizers (Metformin), steroids (for NC-CAH)
GnRHa- Leupride 3.75 mg/ month for three months can be used in severe hirsutism when patient is unable to tolerate OCPs
For more info, Visit : www.medlineacademics.com