Reproductive Endocrinology Prolactin Disorders
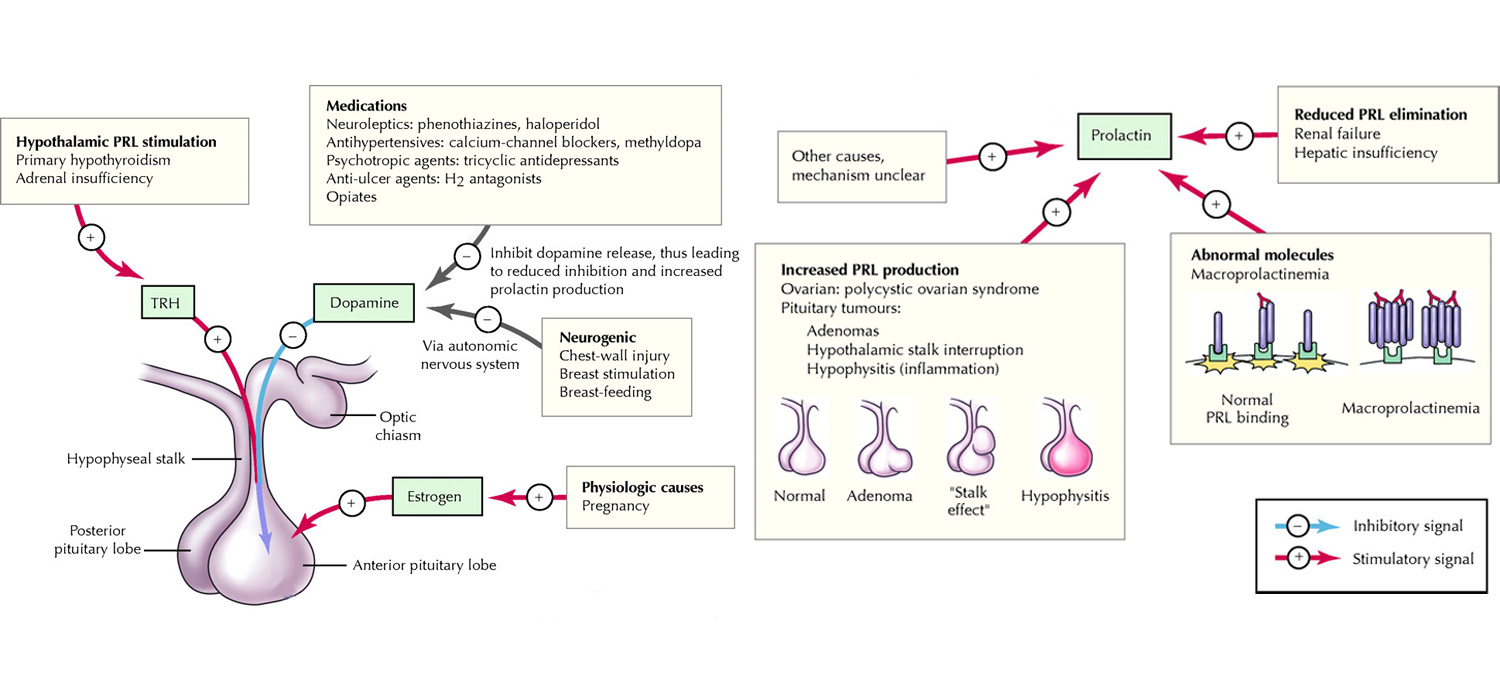
Prolactin is an amino acid hormone, secreted from anterior pituitary and coded on chromosome 6. Unlike other anterior pituitary hormones which are under the influence of releasing factors, prolactin is under inhibitory control. It is suppressed by dopamine while estrogens, TRH. EGF increase prolactin.
The covalently bound dimer form is big prolactin. When it is a polymeric dimer, it is called big big prolactin. Both these cause macroprolactinemia which needs no treatment when It is the solitary findings.
Normal levels are less than 25 micro gms /Lt in women and is a little lower in men. Values over 250 microgms/lt must be evaluated for pituitary tumors.
Causes of hyperprolactinemia
Physiological causes include pregnancy, lactation, stress, nipple stimulation, sleep, coitus, and exercise. Pituitary causes include prolactin adenomas, acromegaly, Cushing’s, empty sella syndrome. CNS tumors, AVMs, auto immune granulomas and mets are the CNS conditions causing raised prolactin. Systemic causes include chronic renal failure, Liver failure (reduce the clearance of prolactin), cranial irradiation, chest wall trauma or herpes zoster. Medications causing raised prolactin are anti-psychotics, anti-emetics (domperidone, metoclopramide), neuroleptics, anti-convulasants and opiates.
Presentation
Hyperprolactinemia is more common amongst women than men. 10% of women with amenorrhea, 25% of women with Galactorrhoea and 70% of women with both have raised levels of prolactin. Women present with Galactorrhoea, oligomenorrhoea, amenorrhea. Reduced libido, luteal phase defects, osteopenia, hypogonadism can also be found in cases of hyperprolactinemia.
Men present with impotence, hypogonadism, infertility, oligospermia, reduced libido, gynecomastia, and gynecomastia. Male impotence secondary to raised prolactin is unresponsive to testosterone and is associated with reduced body hair, low muscle mass and osteoporosis.
Goals of therapy in hyperprolactinemia
- Restoration of normal gonadal function.
- Restoring fertility
- Avoiding osteoporosis
Medical management of hyperprolactinemia
Dopaminergic drugs like bromocriptine (2.5-40 mgms/day) and Cabergoline (0.125-1 mgms twice weekly) are the main drugs. Cabergoline causes better shrinkage of tumors and can be used in bromocriptine resistance or intolerance. Follow up is to repeat the prolactin levels after one month. MRI may be done after a year in microprolactinomas and after 3 months in macroprolactinomas. These medications can be stopped 2 years after normalization of prolactin levels or shrinkage of the tumor. Newer drug like Kisspeptin is being investigated for treatment.
Surgical management of hyperprolactinemia
Surgery is reserved for non-functional tumors causing visual defects, stalk effect and when medical treatment had failed or is not tolerated. Trans-sphenoidal resection is done. 20-50% of macroprolactinomas can recur and merit radiation.
Hyperprolactinemia and pregnancy
Dopaminergic medications are stopped after confirming pregnancy. Bromocriptine may be continued in certain cases like macroadenoma with visual symptoms with no previous surgery or radiation. It is not recommended to estimate prolactin levels in pregnancy.MRI is best avoided during pregnancy. Resistant macroadenomas merit surgery before conception.
For more info, Visit : www.medlineacademics.com