Pre-implantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
What is Pre-implantation Genetic Testing?
Pre-implantation Genetic Testing (PGT) previously known as Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), or pre-implantation genetic screening (PGS) is a procedure performed on the oocytes and embryos to detect genetic abnormality or to know human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing.
What are the types of PGT?
PGT includes PGT-A (pre-implantation genetic testing for aneuploidies, PGT-M (Pre-implantation genetic testing for monogenic disorders or single gene disorders) and PGT-SR (pre-implantation genetic testing for structural chromosomal derangements)
PGT 2.0 is the term sometimes used due to the advent of newer technologies like shifting from Day 3 to Day 5 biopsy, from targeted to genome-wide analysis, robust vitrification methods etc.
What is the process of PGT?
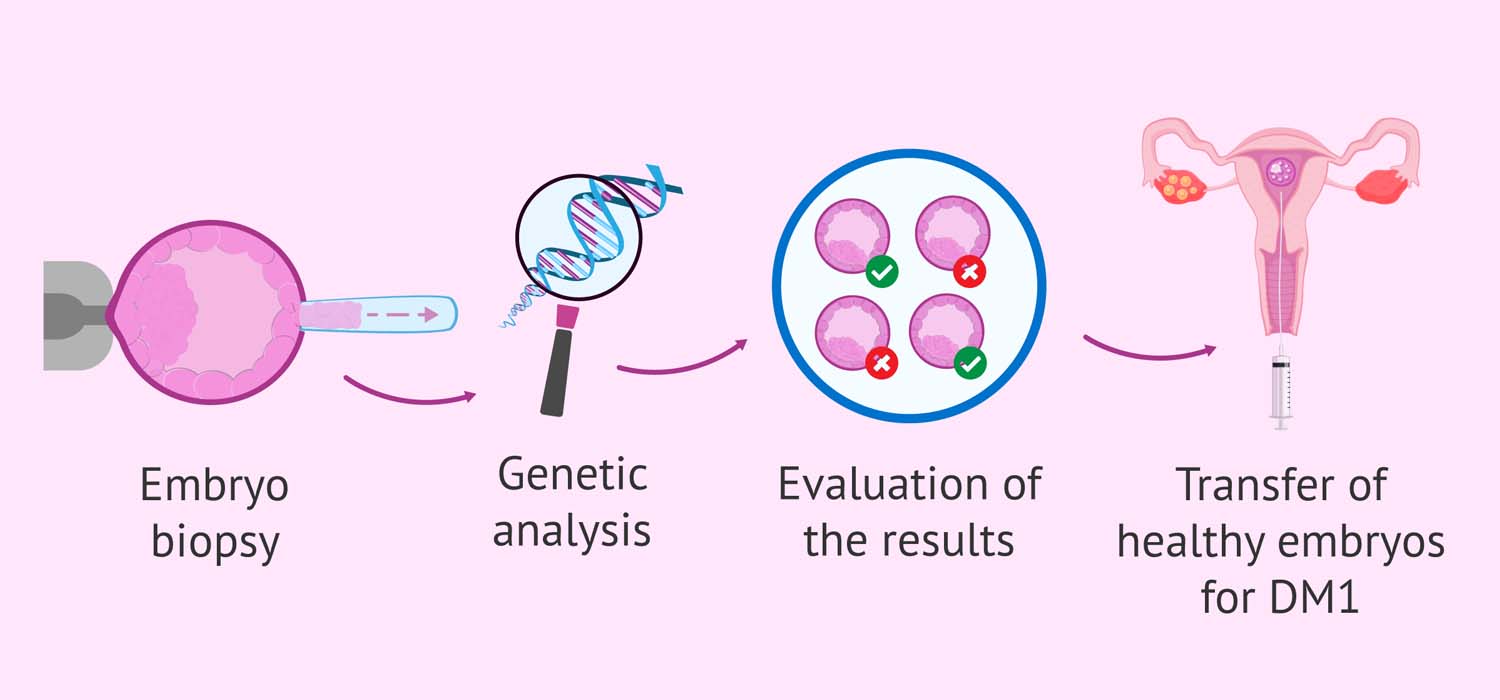
The typical PGT cycle begins with pre-PGT work up and counselling. This especially important because the couple must understand the need for IVF and why a genetic analysis is necessary for the embryo and what the testing will be able to detect. They must also understand that all the embryos may be defective and there will be none for transfer. They must be well counselled by a professional regarding the limitations and possibilities of the test being done.
Case work up and counselling is then followed by IVF, embryo culture followed by embryo biopsy. The biopsy material is then sent for genetic analysis. After the report, frozen embryo transfer is done using the genetically healthy embryo and pregnancy followed up.
What are the advantages of a blastocyst biopsy over the biopsy of a day 3 embryo?
Blastocyst biopsy yields more genetic material than biopsy of Day 3 embryo. (8-10 cells versus 2-3 cells). A day 3 embryo may not culture to a day 5 embryo, but a surviving Day 5 embryo is more advanced in growth. The chance of mosaicism is less with day 5 embryo. Also, the percentage of total cells obtained is more with blastocyst biopsy and hence there is a reduced chance of error. The embryo is not disturbed as the trophectoderm and not the inner cell mass is biopsied.
How is the genetic analysis done?
The first step involves amplifying the genetic material obtained. This can be whole gene amplification or targeted amplification. The second step is analysis of the genetic material obtained. This is done by CGH (Comparative Genomic Hybridization), Array CGH, for SNP (Single nucleotide polymorphism) or NGS (Next Generation Sequencing)
What are the indications of PGT?
PGT-A is indicated in cases of recurrent miscarriage, recurrent implantation failure, advanced maternal age, and severe male factor infertility.
There exist over 1380 single gene disorders, approved by HFEA (Human fertilisation and Embryology Authority- UK regulatory authority) that can be evaluated by PGT-M. In India, this test is mainly done for detecting haematological and musculoskeletal disorders. The common indications include Huntington’s chorea, Cystic fibrosis, Neurofibromatosis, Myotonic dystrophy, Cancer breast/ Ovary, beta-Thalassemia, Fragile-X syndrome, Marphan’s syndrome, Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy etc.
PGT-Sr is indicated for conditions with chromosomal structural rearrangements, Robertsonian translocations, Inversions, or deletions. Pre PGT workup, which is chromosomal analysis of the couple along with the exact structural change, is mandatory before doing PGT-SR. Single cell analysis may be preferred and cleavage stage biopsy may have to be done.
What are the other uses of PGT?
- 1) HLA typing- This can be done along with PGT-M, keeping in mind the ethical concerns (of helping the affected sibling)
- 2) Mitochondrial DNA quantification-Mitochondria do not divide in a cell, till the blastocyst stage. Hence there exists a high mitoscore in slow growing embryos.
What is non-invasive PGT?
Cell free DNA can be detected in spent culture medium (SCM) or blastocyst cavity fluid. This DNA can be extracted, amplified and analysed. This avoids cell sampling of the embryo.
To conclude, PGT is an exciting field that can offer testing of the embryo for various dis-orders. With advances in science, more and more conditions can come under the purview of PGT.
For more info, Visit : www.medlineacademics.com