Chrono-nutrition and it's effect on Male fertility
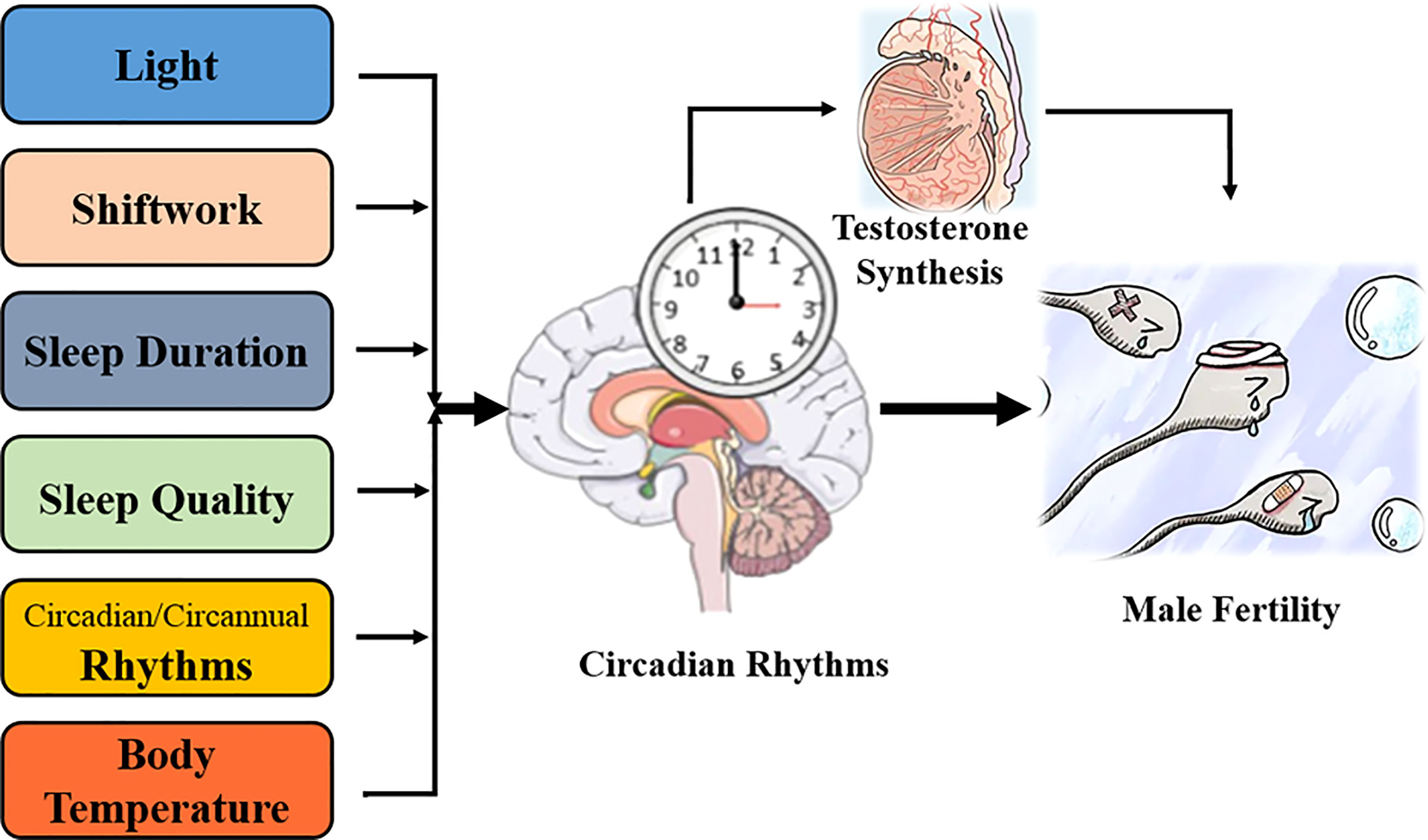
It has been observed that one third of our life is spent in sleeping and that good quality sleep is very important for physiological wellbeing of human beings. Research has shown that there is a strong correlation between sleep disorders and increased risk of mental/metabolic disorders such as depression, diabetes, obesity, infertility etc. Some of the environmental and lifestyle contributors to these condition are sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy food, shift work etc.
During the past quite a few decades there has also been a steady change in the lifestyle and environmental factors such as sleep disturbances, late night snacking, stress, intake of low nutritious and high fat foods and along with it there has been increase in the incidence of infertility. Studies have shown that sleep duration and quality is correlated with reproductive hormonal levels in men and women. Estrogen, progesterone, and androgens are regulated by circadian rhythm and disturbances to the circadian rhythm caused by shift work, late night light exposure, stress, sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy food choices affect the reproductive hormones.
How does light exposure affect male fertility?
With the advent of technology, we spent many hours in front of computers, televisions, and smartphones day in and day out, especially more during the evening hours or shortly prior to sleeping. Thus, our eyes are exposed to artificial light which on long term affects the sleep/wake cycle and disturbed circadian rhythm which in turn affects male fertility by alteration of hormonal levels especially melatonin. Studies have shown that extended light exposure caused decreased testosterone levels, causes abnormal testicular circadian rhythm, and increased oxidative stress.

Is there any relationship between circadian rhythm, body temperature and male fertility?
Our body temperature undergoes a 24-hour rhythmic oscillation in accordance with the day/light and sleep/ wake pattern. It has been shown hyperthermia regulates testicular function by altering clock genes and reproductive hormone levels. It can affect sperm production by altering spermatogenic epithelial structures, promoting testicular oxidative stress and inducing germ cell apoptosis.
How does Chronotypes affect fertility?
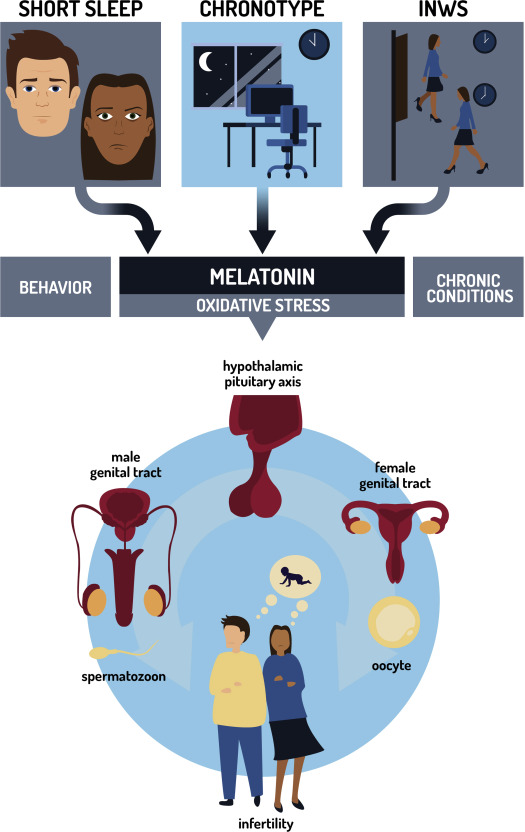
Mammalian circadian clock is synchronized with solar time and cycles every 24 hours. Based on the different patterns in sleep wake cycles people exhibit distinct phenotypes such as chronotypes. Those individuals who go to bed and wake up early have most mental and physical activity in the morning and hence termed as morning chronotype. Those individuals who sleep and wake up late, favour activity during the evening hours, hence they are categorized as evening chronotype. And finally, there are those individuals who are neither morning nor evening type, and lie in between the two, hence termed as intermediate chronotype. It has been observed that people who are evening chronotype had increased incidence of sperm abnormalities such as decreased sperm count, motility when compared to morning type. Similarly, intermediate types showed increased reproductive troubles than morning types.
How does sleep duration affect male fertility?
Several studies were conducted to understand how sleep duration and quality affects male semen parameters. These studies have shown that there is an association between sleep duration and sperm number, concentration, morphology, and motility. In general men who had 7 to 7.5 hours of sleep had highest sperm counts whereas men who were short sleepers (<6 hours) had lower sperm counts, motility and survival when compared to average or long sleepers (>9 hours). It has been shown that in couples who are trying to conceive naturally, there is increased risk of infertility when male partners had a sleep duration of < 6 hours. Men who work on night shift basis has higher incidence of infertility compared to day shift workers. Thus, sleep duration has significant effect on fertility.
Does sleep quality affect male fertility?
Poor sleep quality is associated with increased risk of hypertension, diabetes type 2, cardiovascular disorders, mental disorders, malignancy, and male infertility. Men with lower sleep quality have decreased total sperm count, concentration, motility, and abnormal morphology. It has been suggested that low sleep quality is associated with decreased testosterone production.
What are the different mechanisms by which sleep affects male fertility?
One crucial role of sleep is to maintain bodily function. Disturbances in the sleep can affect the male fertility by many mechanisms, some of them are as follows,
- Testosterone level: Among various reproductive hormones, testosterone is very important in maintaining spermatogenesis. Leydig cells of the testis produce testosterone which exhibits rhythmic oscillations. It has been reported that testosterone levels start to rise at the beginning of sleep and falls during the daytime. Circadian misalignment affects the testosterone’s rhythm and eventually affecting spermatogenesis.
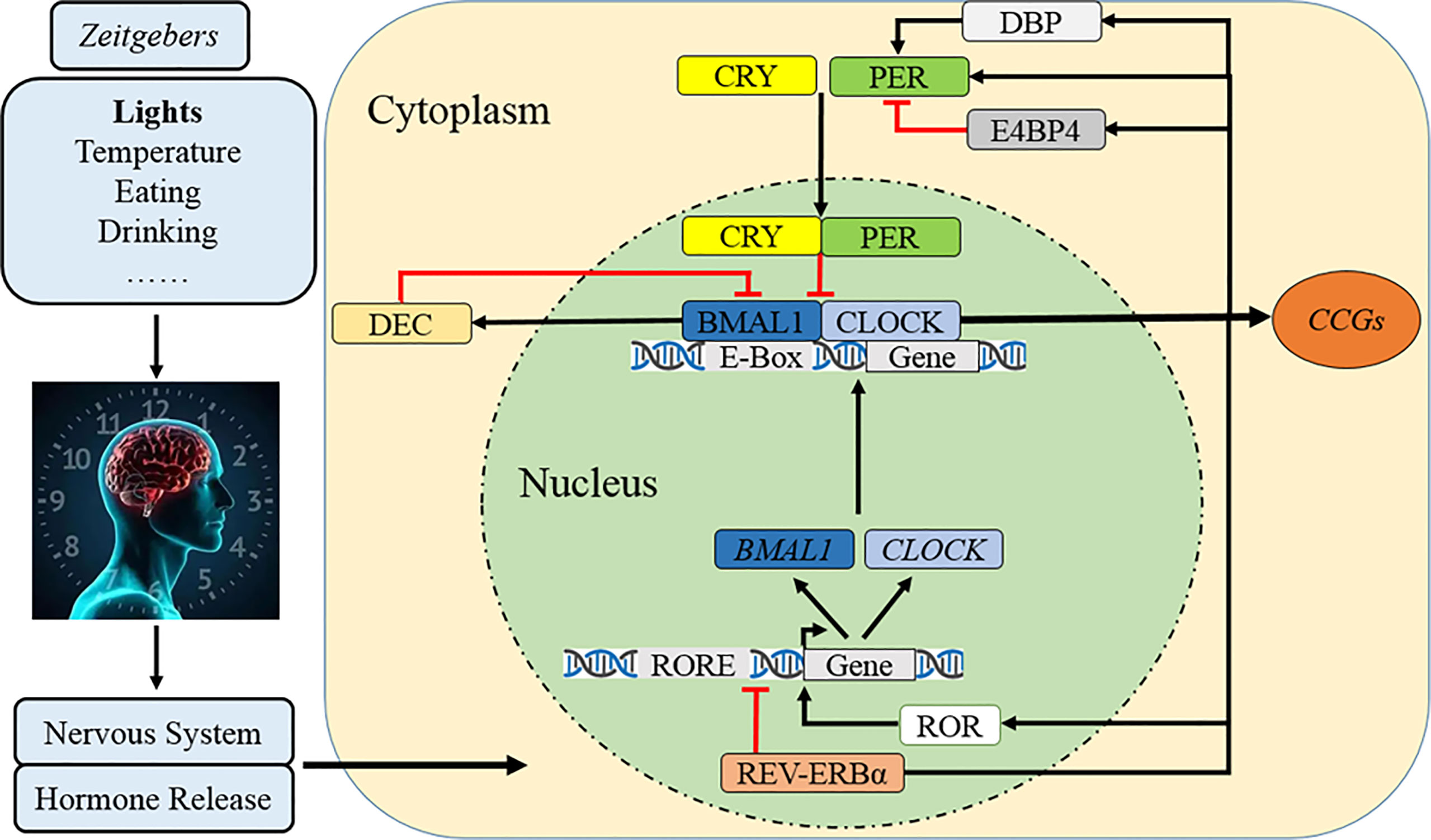
- Circadian clock gene: Many studies have shown that circadian clock genes play a role in the regulation of spermatogenesis. Some of the genes include Bmal1, Per 1/2/3, cry1/2, Rev-erbα/β etc. Disturbances/ mutation/ environmental factors disturbing the circadian clock gene expression could damage spermatogenesis.
- Melatonin: In response to darkness, pineal gland in the brain produces melatonin which is closely related to chronotypes. This hormone production is controlled by circadian rhythm, with high levels at night and lowest in the daytime. Melatonin has regulatory effect on hypothalamus – pituitary testicular axis and thus regulates reproductive physiology. Melatonin is said to influence gonadotropin releasing hormone which in turn acts on the testicle.
- Serotonin: Over the years, serotonin another component of the circadian rhythm has been reported to play important role for normal sperm development.. Animal studies has shown that high levels of serotonin negatively correlated with sperm parameters and could lead to subfertility problems. Recently studies have shown that melatonin also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties at the testicular level. There is also alteration in the behavioural patterns of the individual resulting in sexual dysfunction such as erectile dysfunction.
Does diet affect Male fertility?
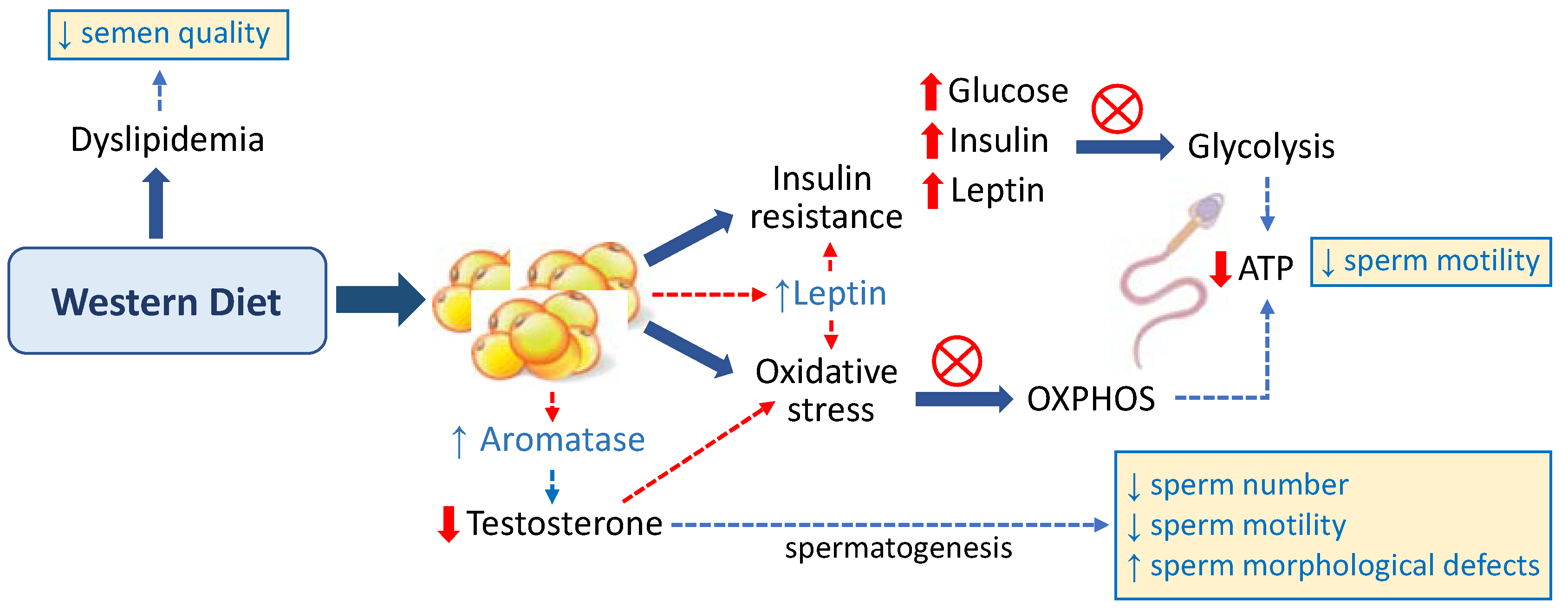
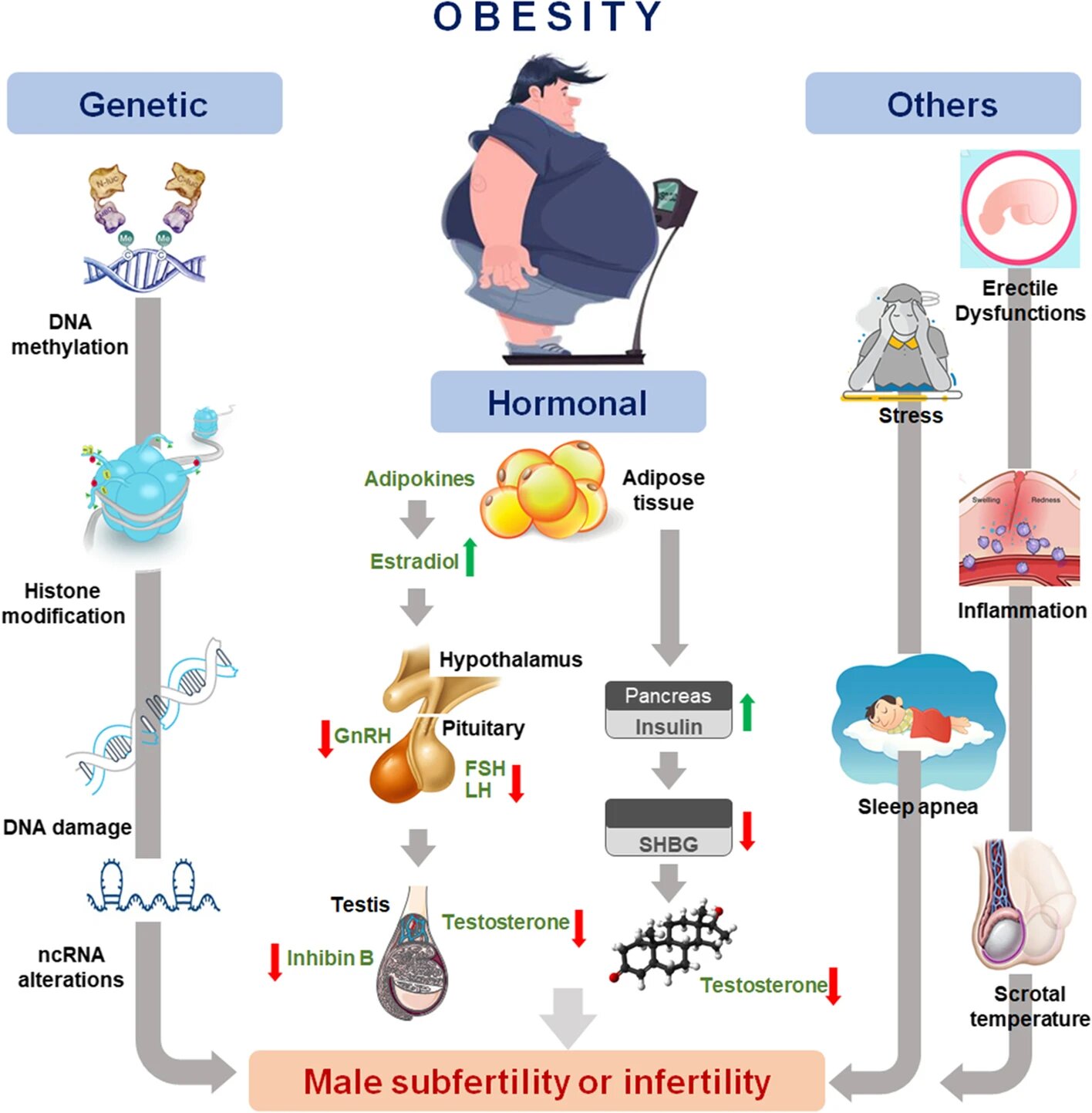
Diet is an important modifiable factor of male reproductive potential. A strong relationship between healthy diet rich in plant diet and fish is correlated with sperm quality. However, disturbance to the nutritional content in long term affects sperm quality. High sugar and high fat diet leads to excess calories and disturbance in the nutrition balance and significantly contributes to obesity, diabetes mellitus, heart disorders, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension etc. Obesity has been reported to affect the hypothalamic-pituitary gonadal axis causing hypogonadism which affects the male hormones testosterone and thus affecting spermatogenesis. Obesity disrupts various factors, some of them are as follows.
- Increased Insulin resistance → impairment of sperm glycolysis → decreased sperm motility.
- Increased leptin alters testicular microenvironment by changing it to proinflammatory state.
- Increased activity of aromatase → decreases testosterone levels.
- Increased oxidative stress → disruption of mitochondrial function → reduction in sperm number and motility.
Conclusion:
With the demands of the modern world along changing lifestyle, there is increase in the incidence of disturbance to our biological circadian rhythm. Numerous studies have shown disturbed sleep quality and duration can lead to male infertility. Nonetheless, more research is needed in this field to better understand the effect of chrono nutrition on male infertility. However, more rational lifestyle with better sleep schedule and timely nutrition could be harnessed as an innovative approach in the field reproductive medicine to help with people with infertility.
Do you want to learn more about different aspects of male infertility and some of the recent advances in the treatment strategies? Enrol in Medline Academics Fellowship in Reproductive Medicine today!
